Quinolones: from antibiotics to autoinducers
- PMID: 20738404
- PMCID: PMC3053476
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00247.x
Quinolones: from antibiotics to autoinducers
Abstract
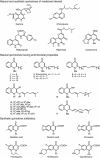
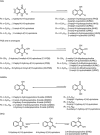
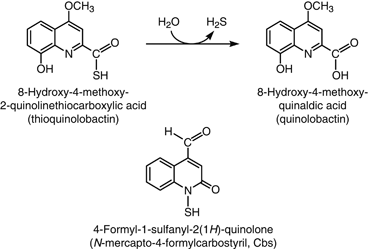
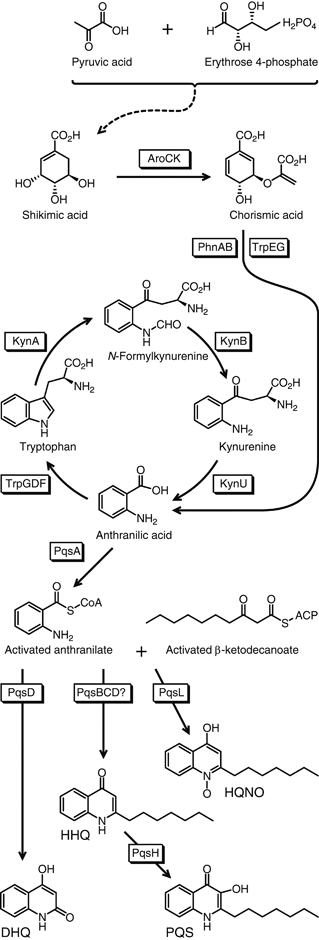
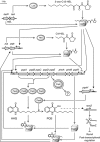
Since quinine was first isolated, animals, plants and microorganisms producing a wide variety of quinolone compounds have been discovered, several of which possess medicinally interesting properties ranging from antiallergenic and anticancer to antimicrobial activities. Over the years, these have served in the development of many synthetic drugs, including the successful fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related bacteria produce a number of 2-alkyl-4(1H)-quinolones, some of which exhibit antimicrobial activity. However, quinolones such as the Pseudomonas quinolone signal and 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline act as quorum-sensing signal molecules, controlling the expression of many virulence genes as a function of cell population density. Here, we review selectively this extensive family of bicyclic compounds, from natural and synthetic antimicrobials to signalling molecules, with a special emphasis on the biology of P. aeruginosa. In particular, we review their nomenclature and biochemistry, their multiple properties as membrane-interacting compounds, inhibitors of the cytochrome bc(1) complex and iron chelators, as well as the regulation of their biosynthesis and their integration into the intricate quorum-sensing regulatory networks governing virulence and secondary metabolite gene expression.
© 2010 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for native agonist and synthetic inhibitor recognition by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing regulator PqsR (MvfR).PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(7):e1003508. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003508. Epub 2013 Jul 25. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23935486 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for Measuring the Production of Quorum Sensing Signal Molecules.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1736:1-15. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7638-6_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29322454
-
Signal Synthase-Type versus Catabolic Monooxygenases: Retracing 3-Hydroxylation of 2-Alkylquinolones and Their N-Oxides by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Other Pulmonary Pathogens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Feb 26;87(6):e02241-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02241-20. Print 2021 Feb 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33452035 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing by 2-alkyl-4-quinolones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacterial species.Mol Biosyst. 2008 Sep;4(9):882-8. doi: 10.1039/b803796p. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 18704225 Review.
-
Relationship between Pyochelin and Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Direction for Future Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 7;25(16):8611. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168611. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201297 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bullied no more: when and how DNA shoves proteins around.Q Rev Biophys. 2012 Aug;45(3):257-299. doi: 10.1017/S0033583512000054. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Q Rev Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22850561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Veterinary Drug Residues in Animal-Derived Foods: Sample Preparation and Analytical Methods.Foods. 2021 Mar 7;10(3):555. doi: 10.3390/foods10030555. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33800096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel targets of the CbrAB/Crc carbon catabolite control system revealed by transcript abundance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e44637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044637. Epub 2012 Oct 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23115619 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal Hierarchy and Context-Dependence of Quorum Sensing Signal in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 22;12(12):1953. doi: 10.3390/life12121953. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556318 Free PMC article.
-
Camphorsulfonic Acid-Mediated One-Pot Tandem Consecutive via the Ugi Four-Component Reaction for the Synthesis of Functionalized Indole and 2-Quinolone Derivatives by Switching Solvents.ACS Omega. 2022 Feb 10;7(7):5713-5729. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05460. eCollection 2022 Feb 22. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35224332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aboul-Fadl T, Fouad EA. Synthesis and in vitro investigations of nalidixic acid amides of amino acid esters as prodrugs. Pharmazie. 1996;51:30–33. - PubMed
-
- Adams DE, Shekhtman EM, Zechiedrich EL, Schmid MB, Cozzarelli NR. The role of topoisomerase IV in partitioning bacterial replicons and the structure of catenated intermediates in DNA replication. Cell. 1992;71:277–288. - PubMed
-
- Aeschlimann JR. The role of multidrug efflux pumps in the antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other Gram-negative bacteria – insights from the society of infectious diseases pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy. 2003;23:916–924. - PubMed
-
- Allesen-Holm M, Barken KB, Yang L, et al. A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol Microbiol. 2006;59:1114–1128. - PubMed
-
- Alon U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:450–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

