Quinolones: from antibiotics to autoinducers
- PMID: 20738404
- PMCID: PMC3053476
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00247.x
Quinolones: from antibiotics to autoinducers
Abstract
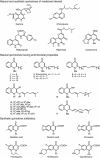
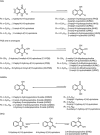
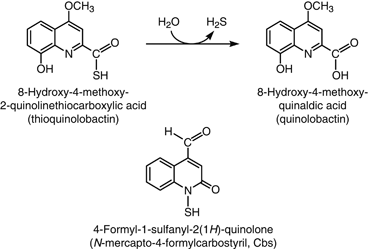
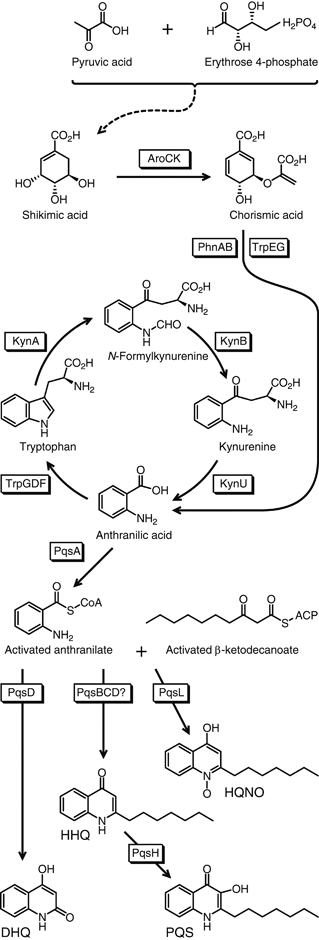
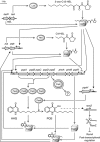
Since quinine was first isolated, animals, plants and microorganisms producing a wide variety of quinolone compounds have been discovered, several of which possess medicinally interesting properties ranging from antiallergenic and anticancer to antimicrobial activities. Over the years, these have served in the development of many synthetic drugs, including the successful fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related bacteria produce a number of 2-alkyl-4(1H)-quinolones, some of which exhibit antimicrobial activity. However, quinolones such as the Pseudomonas quinolone signal and 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline act as quorum-sensing signal molecules, controlling the expression of many virulence genes as a function of cell population density. Here, we review selectively this extensive family of bicyclic compounds, from natural and synthetic antimicrobials to signalling molecules, with a special emphasis on the biology of P. aeruginosa. In particular, we review their nomenclature and biochemistry, their multiple properties as membrane-interacting compounds, inhibitors of the cytochrome bc(1) complex and iron chelators, as well as the regulation of their biosynthesis and their integration into the intricate quorum-sensing regulatory networks governing virulence and secondary metabolite gene expression.
© 2010 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aboul-Fadl T, Fouad EA. Synthesis and in vitro investigations of nalidixic acid amides of amino acid esters as prodrugs. Pharmazie. 1996;51:30–33. - PubMed
-
- Adams DE, Shekhtman EM, Zechiedrich EL, Schmid MB, Cozzarelli NR. The role of topoisomerase IV in partitioning bacterial replicons and the structure of catenated intermediates in DNA replication. Cell. 1992;71:277–288. - PubMed
-
- Aeschlimann JR. The role of multidrug efflux pumps in the antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other Gram-negative bacteria – insights from the society of infectious diseases pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy. 2003;23:916–924. - PubMed
-
- Allesen-Holm M, Barken KB, Yang L, et al. A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol Microbiol. 2006;59:1114–1128. - PubMed
-
- Alon U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:450–461. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

