Interplay of T-cell receptor and interleukin-2 signalling in Vγ2Vδ2 T-cell cytotoxicity
- PMID: 20738419
- PMCID: PMC3015079
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03343.x
Interplay of T-cell receptor and interleukin-2 signalling in Vγ2Vδ2 T-cell cytotoxicity
Abstract
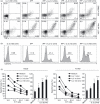
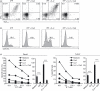
Human peripheral blood Vγ2Vδ2 T cells are important for host defence and tumour immunity. Their unusual T-cell receptor (TCR) recognizes small molecule phosphoantigens; stimulated cells produce inflammatory cytokines and are potently cytotoxic for a variety of tumours. However, molecular mechanisms linking phosphoantigen stimulation and cytotoxicity are incompletely understood. We know that isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) activates mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK/Erk) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI-3K)/Akt pathways; specific inhibition of Erk or Akt significantly impairs the functional response to IPP. We now show that interleukin-2 also activates MEK/Erk and PI-3K/Akt pathways but on its own, fails to induce cytokine expression or cytotoxicity. Hence, MEK/Erk and PI-3K/Akt activation are necessary but not sufficient to induce effector responses in Vγ2Vδ2 T cells and a TCR-dependent signal is still required for tumour cell killing. Cyclosporin A, an inhibitor of calcineurin, blocked calcium-dependent nuclear translocation of nuclear factor of activated T cell (NFAT) and significantly reduced IPP-induced cytokine production, degranulation and cytotoxicity. The IPP-induced calcium mobilization and NFAT translocation were necessary to activate Vγ2Vδ2 effector functions; interleukin-2, acting on the MEK/Erk pathway, regulated the strength of these responses. The TCR has a specific role in Vγ2Vδ2 T-cell killing of tumour cells, which is distinct from its role in triggering cellular proliferation in response to phosphoantigens.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Highly active microbial phosphoantigen induces rapid yet sustained MEK/Erk- and PI-3K/Akt-mediated signal transduction in anti-tumor human gammadelta T-cells.PLoS One. 2009 May 21;4(5):e5657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005657. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19479075 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of classical and novel protein kinase C isoforms in the response of human V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells to phosphate antigens.J Immunol. 2002 Nov 15;169(10):5761-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.5761. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12421956
-
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate, a mycobacterial non-peptidic antigen, triggers delayed and highly sustained signaling in human gamma delta T lymphocytes without inducing eown-modulation of T cell antigen receptor.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 11;276(19):15961-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008684200. Epub 2001 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278429
-
Protective immune responses of major Vγ2Vδ2 T-cell subset in M. tuberculosis infection.Curr Opin Immunol. 2016 Oct;42:105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27491008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional immune responses of HMBPP-specific Vγ2Vδ2 T cells in M. tuberculosis and other infections.Cell Mol Immunol. 2013 Jan;10(1):58-64. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2012.46. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Cell Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23147720 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Five Layers of Receptor Signaling in γδ T-Cell Differentiation and Activation.Front Immunol. 2015 Jan 26;6:15. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00015. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25674089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Memory T cells in the chronic inflammatory microenvironment of nasal polyposis are hyporesponsive to signaling through the T cell receptor.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2012 Jun;13(3):423-35. doi: 10.1007/s10162-012-0313-8. Epub 2012 Feb 4. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 22310933 Free PMC article.
-
The subtle interplay between gamma delta T lymphocytes and dendritic cells: is there a role for a therapeutic cancer vaccine in the era of combinatorial strategies?Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Jul;70(7):1797-1809. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02805-3. Epub 2021 Jan 1. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33386466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis Induced via Gamma Delta T Cell Antigen Receptor "Blocking" Antibodies: A Cautionary Tale.Front Immunol. 2017 Jun 30;8:776. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00776. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28713391 Free PMC article.
-
γδ T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment-Interactions With Other Immune Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 11;13:894315. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.894315. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35880177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carding SR, Egan PJ. γδ T cells: functional plasticity and heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:336–45. - PubMed
-
- Bonneville M, Janeway CA, Jr, Ito K, Haser W, Ishida I, Nakanishi N, Tonegawa S. Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes are a distinct set of γδ T cells. Nature. 1988;336:479–81. - PubMed
-
- Constant P, Davodeau F, Peyrat MA, Poquet Y, Puzo G, Bonneville M, Fournie JJ. Stimulation of human γδ T cells by nonpeptidic mycobacterial ligands. Science. 1994;264:267–70. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka Y, Morita CT, Nieves E, Brenner MB, Bloom BR. Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human γδ T cells. Nature. 1995;375:155–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

