A Pleiotrophin C-terminus peptide induces anti-cancer effects through RPTPβ/ζ
- PMID: 20738847
- PMCID: PMC2936342
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-224
A Pleiotrophin C-terminus peptide induces anti-cancer effects through RPTPβ/ζ
Abstract
Background: Pleiotrophin, also known as HARP (Heparin Affin Regulatory Peptide) is a growth factor expressed in various tissues and cell lines. Pleiotrophin participates in multiple biological actions including the induction of cellular proliferation, migration and angiogenesis, and is involved in carcinogenesis. Recently, we identified and characterized several pleiotrophin proteolytic fragments with biological activities similar or opposite to that of pleiotrophin. Here, we investigated the biological actions of P(122-131), a synthetic peptide corresponding to the carboxy terminal region of this growth factor.
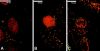
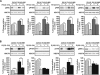
Results: Our results show that P(122-131) inhibits in vitro adhesion, anchorage-independent proliferation, and migration of DU145 and LNCaP cells, which express pleiotrophin and its receptor RPTPβ/ζ. In addition, P(122-131) inhibits angiogenesis in vivo, as determined by the chicken embryo CAM assay. Investigation of the transduction mechanisms revealed that P(122-131) reduces the phosphorylation levels of Src, Pten, Fak, and Erk1/2. Finally, P(122-131) not only interacts with RPTPβ/ζ, but also interferes with other pleiotrophin receptors, as demonstrated by selective knockdown of pleiotrophin or RPTPβ/ζ expression with the RNAi technology.
Conclusions: In conclusion, our results demonstrate that P(122-131) inhibits biological activities that are related to the induction of a transformed phenotype in PCa cells, by interacing with RPTPβ/ζ and interfering with other pleiotrophin receptors. Cumulatively, these results indicate that P(122-131) may be a potential anticancer agent, and they warrant further study of this peptide.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Loss of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase β/ζ (RPTPβ/ζ) promotes prostate cancer metastasis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 23;287(48):40339-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.405852. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23060448 Free PMC article.
-
The synthetic peptide P111-136 derived from the C-terminal domain of heparin affin regulatory peptide inhibits tumour growth of prostate cancer PC-3 cells.BMC Cancer. 2011 May 30;11:212. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-212. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21624116 Free PMC article.
-
A peptide corresponding to the C-terminal region of pleiotrophin inhibits angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro.J Cell Biochem. 2011 Jun;112(6):1532-43. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23066. J Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21344482
-
Pleiotrophin and its receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta as regulators of angiogenesis and cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Dec;1866(2):252-265. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27693125 Review.
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: "Ligand Independent Activation" mediated by the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ signaling pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2219-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23777859 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase β/ζ (RPTPβ/ζ) promotes prostate cancer metastasis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 23;287(48):40339-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.405852. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23060448 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of pleiotrophin in human PC3 prostate cancer cell growth in vivo.Cancer Sci. 2012 Oct;103(10):1826-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02383.x. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22783964 Free PMC article.
-
The synthetic peptide P111-136 derived from the C-terminal domain of heparin affin regulatory peptide inhibits tumour growth of prostate cancer PC-3 cells.BMC Cancer. 2011 May 30;11:212. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-212. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21624116 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotrophin exerts its migration and invasion effect through the neuropilin-1 pathway.Neoplasia. 2015 Aug;17(8):613-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2015.07.007. Neoplasia. 2015. PMID: 26408254 Free PMC article.
-
Midkine: a promising molecule for drug development to treat diseases of the central nervous system.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(5):410-23. doi: 10.2174/138161211795164167. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21375488 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fang W, Hartmann N, Chow DT, Riegel AT, Wellstein A. Pleiotrophin stimulates fibroblasts and endothelial and epithelial cells and is expressed in human cancer. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:25889–25897. - PubMed
-
- Soulie P, Heroult M, Bernard-Pierrot I, Caruelle D, Oglobine J, Barritault D, Courty J. Correlation of elevated plasma levels of two structurally related growth factors, heparin affin regulatory peptide and midkine, in advanced solid tumor patients. Cancer Detect Prev. 2004;28:319–324. doi: 10.1016/j.cdp.2004.03.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

