Arp2/3- and cofilin-coordinated actin dynamics is required for insulin-mediated GLUT4 translocation to the surface of muscle cells
- PMID: 20739464
- PMCID: PMC2954118
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-04-0316
Arp2/3- and cofilin-coordinated actin dynamics is required for insulin-mediated GLUT4 translocation to the surface of muscle cells
Abstract
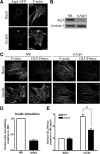
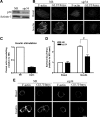
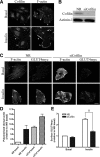
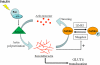
GLUT4 vesicles are actively recruited to the muscle cell surface upon insulin stimulation. Key to this process is Rac-dependent reorganization of filamentous actin beneath the plasma membrane, but the underlying molecular mechanisms have yet to be elucidated. Using L6 rat skeletal myoblasts stably expressing myc-tagged GLUT4, we found that Arp2/3, acting downstream of Rac GTPase, is responsible for the cortical actin polymerization evoked by insulin. siRNA-mediated silencing of either Arp3 or p34 subunits of the Arp2/3 complex abrogated actin remodeling and impaired GLUT4 translocation. Insulin also led to dephosphorylation of the actin-severing protein cofilin on Ser-3, mediated by the phosphatase slingshot. Cofilin dephosphorylation was prevented by strategies depolymerizing remodeled actin (latrunculin B or p34 silencing), suggesting that accumulation of polymerized actin drives severing to enact a dynamic actin cycling. Cofilin knockdown via siRNA caused overwhelming actin polymerization that subsequently inhibited GLUT4 translocation. This inhibition was relieved by reexpressing Xenopus wild-type cofilin-GFP but not the S3E-cofilin-GFP mutant that emulates permanent phosphorylation. Transferrin recycling was not affected by depleting Arp2/3 or cofilin. These results suggest that cofilin dephosphorylation is required for GLUT4 translocation. We propose that Arp2/3 and cofilin coordinate a dynamic cycle of actin branching and severing at the cell cortex, essential for insulin-mediated GLUT4 translocation in muscle cells.
Figures



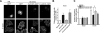
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase Czeta mediates insulin-induced glucose transport through actin remodeling in L6 muscle cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 May;17(5):2322-30. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-10-0969. Epub 2006 Mar 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16525020 Free PMC article.
-
The actin-related p41ARC subunit contributes to p21-activated kinase-1 (PAK1)-mediated glucose uptake into skeletal muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 17;292(46):19034-19043. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.801340. Epub 2017 Sep 25. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28972183 Free PMC article.
-
Cortactin, an actin binding protein, regulates GLUT4 translocation via actin filament remodeling.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011 Nov;76(11):1262-9. doi: 10.1134/S0006297911110083. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2011. PMID: 22117553 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction meets vesicle traffic: the software and hardware of GLUT4 translocation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):C879-86. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00069.2014. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24598362 Review.
-
Rac1 signalling towards GLUT4/glucose uptake in skeletal muscle.Cell Signal. 2011 Oct;23(10):1546-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.05.022. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21683139 Review.
Cited by
-
Putting Rac1 on the path to glucose uptake.Diabetes. 2013 Jun;62(6):1831-2. doi: 10.2337/db13-0381. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23704529 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rac-1 superactivation triggers insulin-independent glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation that bypasses signaling defects exerted by c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)- and ceramide-induced insulin resistance.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 14;288(24):17520-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.467647. Epub 2013 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23640896 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic ROS production by NADPH oxidase 2 regulates muscle glucose uptake during exercise.Nat Commun. 2019 Oct 11;10(1):4623. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12523-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31604916 Free PMC article.
-
A complex of Rab13 with MICAL-L2 and α-actinin-4 is essential for insulin-dependent GLUT4 exocytosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jan 1;27(1):75-89. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-05-0319. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26538022 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 signaling is required for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and is dysregulated in insulin-resistant murine and human skeletal muscle.Diabetes. 2013 Jun;62(6):1865-75. doi: 10.2337/db12-1148. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23423567 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Agnew B. J., Minamide L. S., Bamburg J. R. Reactivation of phosphorylated actin depolymerizing factor and identification of the regulatory site. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:17582–17587. - PubMed
-
- Ashworth S. L., Southgate E. L., Sandoval R. M., Meberg P. J., Bamburg J. R., Molitoris B. A. ADF/cofilin mediates actin cytoskeletal alterations in LLC-PK cells during ATP depletion. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2003;284:F852–F862. - PubMed
-
- Bernards A., Settleman J. GAP control: regulating the regulators of small GTPases. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Bubb M. R., Senderowicz A. M., Sausville E. A., Duncan K. L., Korn E. D. Jasplakinolide, a cytotoxic natural product, induces actin polymerization and competitively inhibits the binding of phalloidin to F-actin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:14869–14871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

