TRPV1 activation is required for hypertonicity-stimulated inflammatory cytokine release in human corneal epithelial cells
- PMID: 20739465
- PMCID: PMC3053292
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-5801
TRPV1 activation is required for hypertonicity-stimulated inflammatory cytokine release in human corneal epithelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: To determine whether hypertonic stress promotes increases in inflammatory cytokine release through transient receptor potential vanilloid channel type 1 (TRPV1) signaling pathway activation in human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs).
Methods: Hyperosmotic medium was prepared by supplementing isotonic Ringers solution with sucrose. Ca2+ signaling was measured in fura2-AM-loaded HCECs using a single-cell fluorescence imaging system. Western blot analysis evaluated the phosphorylation status of EGFR, ERK, p38 MAPK, and nuclear factor (NF)-κB. ELISA assessed the effect of TRPV1 activation on the release of IL-6 and IL-8.
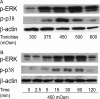
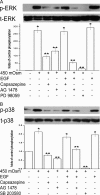
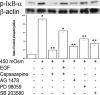
Results: A 450 mOsm hypertonic stress elicited 2-fold Ca2+ transients that were suppressed by the TRPV1-selective antagonists capsazepine and JYL 1421. Such transients were enhanced by PGE2. Hypertonicity-induced EGF receptor (EGFR) transactivation was suppressed by preincubating HCECs with capsazepine, matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) inhibitor TIMP-1, broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor GM 6001, heparin-bound (HB)-EGF inhibitor CRM 197, or EGFR inhibitor AG 1478. ERK and p38 MAPK and NF-κB activation after EGFR transactivation occurred in tonicity and in a time-dependent manner. Hypertonicity-induced increases in IL-6 and IL-8 releases were suppressed by exposure to capsazepine, AG 1478, ERK inhibitor PD 98059, p38 inhibitor SB 203580, or NF-κB inhibitor PDTC.
Conclusions: Hypertonic stress-elicited TRPV1 channel stimulation mediates increases in a proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 and a chemoattractant IL-8 by eliciting EGFR transactivation, MAPK, and NF-κB activation. Selective drug modulation of either TRPV1 activity or its signaling mediators may yield a novel approach to suppressing inflammatory responses occurring in dry eye syndrome.
Figures





References
-
- Luo L, Li DQ, Corrales RM, Pflugfelder SC. Hyperosmolar saline is a proinflammatory stress on the mouse ocular surface. Eye Contact Lens. 2005;31:186–193 - PubMed
-
- Tomlinson A, Khanal S, Ramaesh K, Diaper C, McFadyen A. Tear film osmolarity: determination of a referent for dry eye diagnosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47:4309–4315 - PubMed
-
- Gilbard JP, Kenyon KR. Tear diluents in the treatment of keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Ophthalmology. 1985;92:646–650 - PubMed
-
- Papa V, Aragona P, Russo S, Di Bella A, Russo P, Milazzo G. Comparison of hypotonic and isotonic solutions containing sodium hyaluronate on the symptomatic treatment of dry eye patients. Ophthalmologica. 2001;215:124–127 - PubMed
-
- Alessandri-Haber N, Yeh JJ, Boyd AE, et al. Hypotonicity induces TRPV4-mediated nociception in rat. Neuron. 2003;39:497–511 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

