Impact of viral-mediated IGF-I gene transfer on skeletal muscle following cast immobilization
- PMID: 20739512
- PMCID: PMC2980362
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00230.2010
Impact of viral-mediated IGF-I gene transfer on skeletal muscle following cast immobilization
Abstract
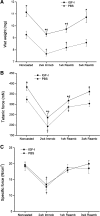
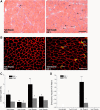
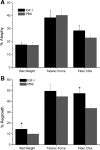
Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is a potent myogenic factor that plays a critical role in muscle regeneration and muscle hypertrophy. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of IGF-I overexpression on the recovery of muscle size and function during reloading/reambulation after a period of cast immobilization in predominantly fast twitch muscles. In addition, we investigated concomitant molecular responses in IGF-I receptor and binding proteins (BPs). Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector for IGF-I (rAAV-IGF-IA) was injected into the anterior compartment of one of the hindlimbs of young (3 wk) C57BL6 female mice. At 20 wk of age, both hindlimbs were cast immobilized in a shortened position for 2 wk to unload the tibialis anterior (TA) and extensor longus digitorum (EDL) muscles. The TA and EDL muscles were removed bilaterally after 2 wk of cast immobilization and after 1 and 3 wk of free cage reambulation. Increases in IGF-I mRNA and protein levels with IGF-I overexpression were associated with significant increases in muscle wet weight, fiber size, and tetanic force, although overexpression did not protect against cast immobilization-induced muscle atrophy. After 1 wk of reambulation, evidence of enhanced muscle regeneration was noted in IGF-I-overexpressing muscles with an increased prevalence of central nuclei, embryonic myosin, and Pax7 positive fibers. We also observed larger relative gains in muscle size (wet weight and fiber area), but not force, during the 3-wk reambulation period in hindlimb muscles overexpressing IGF-I compared with contralateral control legs. Changes in IGFBP-5 mRNA expression during cast immobilization and reambulation paralleled those of IGF-I, whereas IGFBP-3 expression changed inversely to IGFBP-5.
Figures




References
-
- Adams GR. Role of insulin-like growth factor-I in the regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation to increased loading. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 26: 31–60, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Adams GR, Caiozzo VJ, Haddad F, Baldwin KM. Cellular and molecular responses to increased skeletal muscle loading after irradiation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283: C1182–C1195, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Adams GR, Haddad F. The relationships among IGF-1, DNA content, and protein accumulation during skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol 81: 2509–2516, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Adams GR, McCue SA. Localized infusion of IGF-I results in skeletal muscle hypertrophy in rats. J Appl Physiol 84: 1716–1722, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Andress DL, Birnbaum RS. Human osteoblast-derived insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-5 stimulates osteoblast mitogenesis and potentiates IGF action. J Biol Chem 267: 22467–22472, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

