Ataxin-2 intermediate-length polyglutamine expansions are associated with increased risk for ALS
- PMID: 20740007
- PMCID: PMC2965417
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09320
Ataxin-2 intermediate-length polyglutamine expansions are associated with increased risk for ALS
Abstract
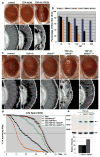
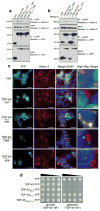
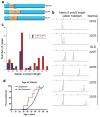
The causes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a devastating human neurodegenerative disease, are poorly understood, although the protein TDP-43 has been suggested to have a critical role in disease pathogenesis. Here we show that ataxin 2 (ATXN2), a polyglutamine (polyQ) protein mutated in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2, is a potent modifier of TDP-43 toxicity in animal and cellular models. ATXN2 and TDP-43 associate in a complex that depends on RNA. In spinal cord neurons of ALS patients, ATXN2 is abnormally localized; likewise, TDP-43 shows mislocalization in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. To assess the involvement of ATXN2 in ALS, we analysed the length of the polyQ repeat in the ATXN2 gene in 915 ALS patients. We found that intermediate-length polyQ expansions (27-33 glutamines) in ATXN2 were significantly associated with ALS. These data establish ATXN2 as a relatively common ALS susceptibility gene. Furthermore, these findings indicate that the TDP-43-ATXN2 interaction may be a promising target for therapeutic intervention in ALS and other TDP-43 proteinopathies.
Figures


Comment in
-
Neurodegeneration: An expansion in ALS genetics.Nature. 2010 Aug 26;466(7310):1052-3. doi: 10.1038/4661052a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20740002 No abstract available.
-
'Forward genetics' and the causes of ALS.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Feb;20(2):67. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0062-6. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30279566 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AG017586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01NS065317-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AG-10124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1DP2OD004417-01/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG-033101-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065317/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD004417/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG-17586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG009215/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG-09215/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG033101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

