Retinal proteomic changes under different ischemic conditions - implication of an epigenetic regulatory mechanism
- PMID: 20740046
- PMCID: PMC2926809
Retinal proteomic changes under different ischemic conditions - implication of an epigenetic regulatory mechanism
Abstract
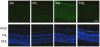
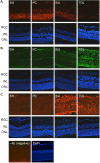
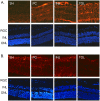
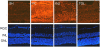
In retina, an ischemic injury-resistant condition (ischemic tolerance) can be induced by a sub-lethal ischemic treatment (preconditioning) prior to an otherwise injurious ischemic insult. In this work, we compared retinal proteomic changes under three different ischemic conditions, as a means to identify the effector mechanisms that underlie retinal ischemic tolerance. Transient retinal ischemia was induced by elevating the intraocular pressure (IOP) in three groups of adult rats as follows: Group 1, ischemic-preconditioned, 110 mmHg for 8 minutes followed by 48 hours reperfusion; Group 2, ischemic-injured, 110 mmHg for 60 minutes followed by 24 hours reperfusion; Group 3, ischemic-tolerant, preconditioning treatment followed by another 60 minutes of 110 mmHg and 24 hours reperfusion. Protein quantities in each of the afore-mentioned retinal ischemic conditions, as determined by quantitative mass spectrometry, were compared with that of the contralateral control eyes (sham-treated). As a result, a total of 328 proteins were identified and quantified; among them, 30-60% of proteins showed a change in abundance under one or more retinal ischemic conditions. In particular, in ischemic-tolerant retinas, histone proteins H2B, H3 and H4 demonstrated an increase in abundance, whereas histone H2A showed a decrease in abundance. Further immunohistochemical analyses confirmed the results of proteomic analyses, and detected an up regulation of tri-methylated histone H3, mono-ubiquitinated histone H2A and Polycomb group protein RING2. Together, these results suggest a role of epigenetic regulation in the induction of retinal ischemic tolerance that involves histone and polycomb proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Roth S, Li B, Rosenbaum PS, Gupta H, Goldstein IM, Maxwell KM, Gidday JM. Preconditioning provides complete protection against retinal ischemic injury in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39(5):777–85. - PubMed
-
- Zhang C, Rosenbaum DM, Shaikh AR, Li Q, Rosenbaum PS, Pelham DJ, Roth S. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates apoptotic cell death in the rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43(9):3059–66. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Ojwang BA, Brantley MA, Gidday JM., Jr Long-term tolerance to retinal ischemia by repetitive hypoxic preconditioning: role of HIF-1alpha and heme oxygenase-1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48(4):1735–43. - PubMed
-
- Kamphuis W, Dijk F, Bergen AA. Ischemic preconditioning alters the pattern of gene expression changes in response to full retinal ischemia. Mol Vis. 2007;13:1892–901. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
