Characterization of Atrophic Changes in the Cerebral Cortex Using Fractal Dimensional Analysis
- PMID: 20740072
- PMCID: PMC2927230
- DOI: 10.1007/s11682-008-9057-9
Characterization of Atrophic Changes in the Cerebral Cortex Using Fractal Dimensional Analysis
Abstract
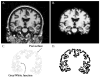
The purpose of this project is to apply a modified fractal analysis technique to high-resolution T1 weighted magnetic resonance images in order to quantify the alterations in the shape of the cerebral cortex that occur in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Images were selected from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative database (Control N=15, Mild-Moderate AD N=15). The images were segmented using a semi-automated analysis program. Four coronal and three axial profiles of the cerebral cortical ribbon were created. The fractal dimensions (D(f)) of the cortical ribbons were then computed using a box-counting algorithm. The mean D(f) of the cortical ribbons from AD patients were lower than age-matched controls on six of seven profiles. The fractal measure has regional variability which reflects local differences in brain structure. Fractal dimension is complementary to volumetric measures and may assist in identifying disease state or disease progression.
Figures




References
-
- Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Flory J, Damasio AR, Van Hoesen GW. The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Cerebral Cortex (New York, NY) 1991;1(1):103–116. doi: 10.1093/cercor/1.1.103. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Casanova MF, Goldberg TE, Suddath RL, Daniel DG, Rawlings R, Lloyd DG, et al. Quantitative shape analysis of the temporal and prefrontal lobes of schizophrenic patients: A magnetic resonance image study. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 1990;2(4):363–372. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
