Accelerated cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the mouse using an eight-channel array at 9.4 Tesla
- PMID: 20740650
- PMCID: PMC3021721
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22605
Accelerated cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the mouse using an eight-channel array at 9.4 Tesla
Abstract
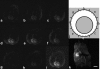
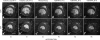
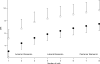
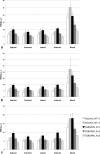
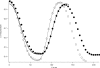
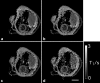
MRI has become an important tool to noninvasively assess global and regional cardiac function, infarct size, or myocardial blood flow in surgically or genetically modified mouse models of human heart disease. Constraints on scan time due to sensitivity to general anesthesia in hemodynamically compromised mice frequently limit the number of parameters available in one imaging session. Parallel imaging techniques to reduce acquisition times require coil arrays, which are technically challenging to design at ultrahigh magnetic field strengths. This work validates the use of an eight-channel volume phased-array coil for cardiac MRI in mice at 9.4 T. Two- and three-dimensional sequences were combined with parallel imaging techniques and used to quantify global cardiac function, T(1)-relaxation times and infarct sizes. Furthermore, the rapid acquisition of functional cine-data allowed for the first time in mice measurement of left-ventricular peak filling and ejection rates under intravenous infusion of dobutamine. The results demonstrate that a threefold accelerated data acquisition is generally feasible without compromising the accuracy of the results. This strategy may eventually pave the way for routine, multiparametric phenotyping of mouse hearts in vivo within one imaging session of tolerable duration.
© 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Streif JU, Herold V, Szimtenings M, Lanz TE, Nahrendorf M, Wiesmann F, Rommel E, Haase A. In vivo time-resolved quantitative motion mapping of the murine myocardium with phase contrast MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49:315–321. - PubMed
-
- Herold V, Morchel P, Faber C, Rommel E, Haase A, Jakob PM. In vivo quantitative three-dimensional motion mapping of the murine myocardium with PC-MRI at 17.6 T. Magn Reson Med. 2006;55:1058–1064. - PubMed
-
- Epstein FH, Yang Z, Gilson WD, Berr SS, Kramer CM, French BA. MR tagging early after myocardial infarction in mice demonstrates contractile dysfunction in adjacent and remote regions. Magn Reson Med. 2002;48:399–403. - PubMed
-
- Gilson WD, Yang Z, French BA, Epstein FH. Measurement of myocardial mechanics in mice before and after infarction using multislice displacement-encoded MRI with 3D motion encoding. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H1491–H1497. - PubMed
-
- Kober F, Iltis I, Cozzone PJ, Bernard M. Myocardial blood flow mapping in mice using high-resolution spin labeling magnetic resonance imaging: influence of ketamine/xylazine and isoflurane anesthesia. Magn Reson Med. 2005;53:601–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

