Simulation of two-dimensional ultraviolet spectroscopy of amyloid fibrils
- PMID: 20795695
- PMCID: PMC2953465
- DOI: 10.1021/jp1046968
Simulation of two-dimensional ultraviolet spectroscopy of amyloid fibrils
Abstract
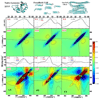
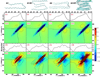
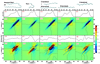
Revealing the structure and aggregation mechanism of amyloid fibrils is essential for the treatment of over 20 diseases related to protein misfolding. Coherent two-dimensional (2D) infrared spectroscopy is a novel tool that provides a wealth of new insight into the structure and dynamics of biomolecular systems. Recently developed ultrafast laser sources are extending multidimensional spectroscopy into the ultraviolet (UV) region, and this opens up new opportunities for probing fibrils. In a simulation study, we show that 2DUV spectra of the backbone of a 32-residue β-amyloid (Aβ(9-40)) fibril associated with Alzheimer's disease and two intermediate prefibrillar structures carry characteristic signatures of fibril size and geometry that could be used to monitor its formation kinetics. The dependence of these signals on the fibril size and geometry is explored. We demonstrate that the dominant features of the β-amyloid fibril spectra are determined by intramolecular interactions within a single Aβ(9-40), and intermolecular interactions at the "external interface" have clear signatures in the fine details of these signals.
Figures
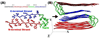

Similar articles
-
Distinguishing amyloid fibril structures in Alzheimer's disease (AD) by two-dimensional ultraviolet (2DUV) spectroscopy.Biochemistry. 2011 Nov 15;50(45):9809-16. doi: 10.1021/bi201317c. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21961527 Free PMC article.
-
Probing amyloid fibril growth by two-dimensional near-ultraviolet spectroscopy.J Phys Chem B. 2011 May 19;115(19):6321-8. doi: 10.1021/jp201164u. Epub 2011 Apr 25. J Phys Chem B. 2011. PMID: 21517033 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking the mechanism of fibril assembly by simulated two-dimensional ultraviolet spectroscopy.J Phys Chem A. 2013 Jan 17;117(2):342-50. doi: 10.1021/jp3101267. Epub 2013 Jan 7. J Phys Chem A. 2013. PMID: 23214934 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies on the Aggregation of Amyloid-β Peptides and Their Disaggregation by Ultrasonic Wave and Infrared Laser Irradiation.Molecules. 2022 Apr 12;27(8):2483. doi: 10.3390/molecules27082483. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35458686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding amyloid fibril nucleation and aβ oligomer/drug interactions from computer simulations.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Feb 18;47(2):603-11. doi: 10.1021/ar4002075. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24368046 Review.
Cited by
-
Two-dimensional ultraviolet (2DUV) spectroscopic tools for identifying fibrillation propensity of protein residue sequences.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010 Dec 10;49(50):9666-9. doi: 10.1002/anie.201005093. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2010. PMID: 21077077 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Two-dimensional near-ultraviolet spectroscopy of aromatic residues in amyloid fibrils: a first principles study.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011 Feb 14;13(6):2394-400. doi: 10.1039/c0cp02047h. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011. PMID: 21132201 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the γD-crystallin protein using two-dimensional infrared (2DIR) spectroscopy: experiment and simulation.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Dec 12;117(49):15436-43. doi: 10.1021/jp405159v. Epub 2013 Sep 18. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23972032 Free PMC article.
-
Distinguishing amyloid fibril structures in Alzheimer's disease (AD) by two-dimensional ultraviolet (2DUV) spectroscopy.Biochemistry. 2011 Nov 15;50(45):9809-16. doi: 10.1021/bi201317c. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21961527 Free PMC article.
-
Probing amyloid fibril growth by two-dimensional near-ultraviolet spectroscopy.J Phys Chem B. 2011 May 19;115(19):6321-8. doi: 10.1021/jp201164u. Epub 2011 Apr 25. J Phys Chem B. 2011. PMID: 21517033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tycko R. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004;14:96–103. - PubMed
-
- Caughey B, Lansbury PT. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2003;26:267–298. - PubMed
-
- Lester-Coll NE, Riviera EJ, Soscia SJ, Doiron K, Wands JR, de la Monte SM. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9:13–33. - PubMed
-
- Glabe C, Kayed R. Neurology. 2006;66:S74–S78. - PubMed
-
- Chiti F, Dobson CM. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006;75:333–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

