A standard variation file format for human genome sequences
- PMID: 20796305
- PMCID: PMC2945790
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r88
A standard variation file format for human genome sequences
Abstract
Here we describe the Genome Variation Format (GVF) and the 10Gen dataset. GVF, an extension of Generic Feature Format version 3 (GFF3), is a simple tab-delimited format for DNA variant files, which uses Sequence Ontology to describe genome variation data. The 10Gen dataset, ten human genomes in GVF format, is freely available for community analysis from the Sequence Ontology website and from an Amazon elastic block storage (EBS) snapshot for use in Amazon's EC2 cloud computing environment.
Figures
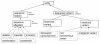

References
-
- Levy S, Sutton G, Ng PC, Feuk L, Halpern AL, Walenz BP, Axelrod N, Huang J, Kirkness EF, Denisov G, Lin Y, MacDonald JR, Pang AW, Shago M, Stockwell TB, Tsiamouri A, Bafna V, Bansal V, Kravitz SA, Busam DA, Beeson KY, McIntosh TC, Remington KA, Abril JF, Gill J, Borman J, Rogers YH, Frazier ME, Scherer SW, Strausberg RL. et al.The diploid genome sequence of an individual human. PLoS Biol. 2007;5:e254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050254. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wheeler DA, Srinivasan M, Egholm M, Shen Y, Chen L, McGuire A, He W, Chen YJ, Makhijani V, Roth GT, Gomes X, Tartaro K, Niazi F, Turcotte CL, Irzyk GP, Lupski JR, Chinault C, Song XZ, Liu Y, Yuan Y, Nazareth L, Qin X, Muzny DM, Margulies M, Weinstock GM, Gibbs RA, Rothberg JM. The complete genome of an individual by massively parallel DNA sequencing. Nature. 2008;452:872–876. doi: 10.1038/nature06884. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McKernan KJ, Peckham HE, Costa GL, McLaughlin SF, Fu Y, Tsung EF, Clouser CR, Duncan C, Ichikawa JK, Lee CC, Zhang Z, Ranade SS, Dimalanta ET, Hyland FC, Sokolsky TD, Zhang L, Sheridan A, Fu H, Hendrickson CL, Li B, Kotler L, Stuart JR, Malek JA, Manning JM, Antipova AA, Perez DS, Moore MP, Hayashibara KC, Lyons MR, Beaudoin RE. et al.Sequence and structural variation in a human genome uncovered by short-read, massively parallel ligation sequencing using two-base encoding. Genome Res. 2009;19:1527–1541. doi: 10.1101/gr.091868.109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bentley DR, Balasubramanian S, Swerdlow HP, Smith GP, Milton J, Brown CG, Hall KP, Evers DJ, Barnes CL, Bignell HR, Boutell JM, Bryant J, Carter RJ, Keira Cheetham R, Cox AJ, Ellis DJ, Flatbush MR, Gormley NA, Humphray SJ, Irving LJ, Karbelashvili MS, Kirk SM, Li H, Liu X, Maisinger KS, Murray LJ, Obradovic B, Ost T, Parkinson ML, Pratt MR. et al.Accurate whole human genome sequencing using reversible terminator chemistry. Nature. 2008;456:53–59. doi: 10.1038/nature07517. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Wang W, Li R, Li Y, Tian G, Goodman L, Fan W, Zhang J, Li J, Guo Y, Feng B, Li H, Lu Y, Fang X, Liang H, Du Z, Li D, Zhao Y, Hu Y, Yang Z, Zheng H, Hellmann I, Inouye M, Pool J, Yi X, Zhao J, Duan J, Zhou Y, Qin J, Ma L. et al.The diploid genome sequence of an Asian individual. Nature. 2008;456:60–65. doi: 10.1038/nature07484. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

