Activity-based profiling reveals reactivity of the murine thymoproteasome-specific subunit beta5t
- PMID: 20797608
- PMCID: PMC3039300
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.05.027
Activity-based profiling reveals reactivity of the murine thymoproteasome-specific subunit beta5t
Abstract
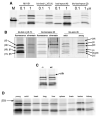
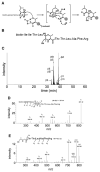
Epithelial cells of the thymus cortex express a unique proteasome particle involved in positive T cell selection. This thymoproteasome contains the recently discovered beta5t subunit that has an uncharted activity, if any. We synthesized fluorescent epoxomicin probes that were used in a chemical proteomics approach, entailing activity-based profiling, affinity purification, and LC-MS identification, to demonstrate that the beta5t subunit is catalytically active in the murine thymus. A panel of established proteasome inhibitors showed that the broad-spectrum inhibitor epoxomicin blocks the beta5t activity and that the subunit-specific antagonists bortezomib and NC005 do not inhibit beta5t. We show that beta5t has a substrate preference distinct from beta5/beta5i that might explain how the thymoproteasome generates the MHC class I peptide repertoire needed for positive T cell selection.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adams J, Behnke M, Chen S, Cruickshank AA, Dick LR, Grenier L, Klunder JM, Ma YT, Plamondon L, Stein RL. Potent and selective inhibitors of the proteasome: dipeptidyl boronic acids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1998;8:333–338. - PubMed
-
- Baumeister W, Walz J, Zuhl F, Seemuller E. The proteasome: paradigm of a self-compartmentalizing protease. Cell. 1998;92:367–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

