Application of fragment-based drug discovery to membrane proteins: identification of ligands of the integral membrane enzyme DsbB
- PMID: 20797617
- PMCID: PMC4104428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.06.011
Application of fragment-based drug discovery to membrane proteins: identification of ligands of the integral membrane enzyme DsbB
Abstract
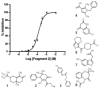
Membrane proteins are important pharmaceutical targets, but they pose significant challenges for fragment-based drug discovery approaches. Here, we present the first successful use of biophysical methods to screen for fragment ligands to an integral membrane protein. The Escherichia coli inner membrane protein DsbB was solubilized in detergent micelles and lipid bilayer nanodiscs. The solubilized protein was immobilized with retention of functionality and used to screen 1071 drug fragments for binding using target immobilized NMR Screening. Biochemical and biophysical validation of the eight most potent hits revealed an IC(50) range of 7-200 microM. The ability to insert a broad array of membrane proteins into nanodiscs, combined with the efficiency of TINS, demonstrates the feasibility of finding fragments targeting membrane proteins.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
G.S. acknowledges greater than 5% ownership in a company, ZoBio BV, whose goal is to commercialize TINS-based drug discovery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Target immobilization as a strategy for NMR-based fragment screening: comparison of TINS, STD, and SPR for fragment hit identification.J Biomol Screen. 2010 Sep;15(8):978-89. doi: 10.1177/1087057110375614. J Biomol Screen. 2010. PMID: 20817886
-
Target immobilization and NMR screening of fragments in early drug discovery.Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(18):1736-45. doi: 10.2174/156802609790102400. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19929836
-
Integrated biophysical approach to fragment screening and validation for fragment-based lead discovery.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 6;110(32):12984-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304045110. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23872845 Free PMC article.
-
NMR in drug discovery on membrane proteins.Future Med Chem. 2012 May;4(7):869-75. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.46. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22571612 Review.
-
Solution NMR Spectroscopy in Target-Based Drug Discovery.Molecules. 2017 Aug 23;22(9):1399. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091399. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28832542 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanodisc-based co-immunoprecipitation for mass spectrometric identification of membrane-interacting proteins.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Jul;10(7):O110.006775. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O110.006775. Epub 2011 Apr 30. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21532009 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence of the Melioidosis Pathogen Burkholderia pseudomallei Requires the Oxidoreductase Membrane Protein DsbB.Infect Immun. 2018 Apr 23;86(5):e00938-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00938-17. Print 2018 May. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29440370 Free PMC article.
-
NMR structures of membrane proteins in phospholipid bilayers.Q Rev Biophys. 2014 Aug;47(3):249-83. doi: 10.1017/S0033583514000080. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Q Rev Biophys. 2014. PMID: 25032938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nature of Nanodisc Lipids Influences Fragment-Based Drug Discovery Results.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2025 Mar;105(3):e70080. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.70080. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 40087816 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysics in drug discovery: impact, challenges and opportunities.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Oct;15(10):679-98. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.123. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27516170 Review.
References
-
- Zheng CJ, Han L, Yap CW, Xie B, Chen YZ. Progress and problems in the exploration of therapeutic targets (vol 11, pg 412, 2006) Drug Discovery Today. 2006;11:717. - PubMed
-
- Carr RAE, Congreve M, Murray CW, Rees DC. Fragment-based lead discovery: leads by design. Drug Discovery Today. 2005;10:987–992. - PubMed
-
- Congreve M, Carr R, Murray C, Jhoti H. A rule of three for fragment-based lead discovery? Drug Discovery Today. 2003;8:876–877. - PubMed
-
- Siegal G, ABE, Schultz J. Integration of fragment screening and library design. Drug Discovery Today. 2007;12:1032–1039. - PubMed
-
- Hajduk PJ, Meadows RP, Fesik SW. Drug design - Discovering high-affinity ligands for proteins. Science. 1997;278:497–499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

