Modulation of pantothenate kinase 3 activity by small molecules that interact with the substrate/allosteric regulatory domain
- PMID: 20797618
- PMCID: PMC2929395
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.06.006
Modulation of pantothenate kinase 3 activity by small molecules that interact with the substrate/allosteric regulatory domain
Abstract
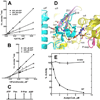
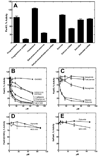
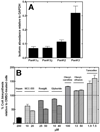
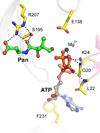
Pantothenate kinase (PanK) catalyzes the rate-controlling step in coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthesis. PanK3 is stringently regulated by acetyl-CoA and uses an ordered kinetic mechanism with ATP as the leading substrate. Biochemical analysis of site-directed mutants indicates that pantothenate binds in a tunnel adjacent to the active site that is occupied by the pantothenate moiety of the acetyl-CoA regulator in the PanK3acetyl-CoA binary complex. A high-throughput screen for PanK3 inhibitors and activators was applied to a bioactive compound library. Thiazolidinediones, sulfonylureas and steroids were inhibitors, and fatty acyl-amides and tamoxifen were activators. The PanK3 activators and inhibitors either stimulated or repressed CoA biosynthesis in HepG2/C3A cells. The flexible allosteric acetyl-CoA regulatory domain of PanK3 also binds the substrates, pantothenate and pantetheine, and small molecule inhibitors and activators to modulate PanK3 activity.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bell DS. Practical considerations and guidelines for dosing sulfonylureas as monotherapy or combination therapy. Clin. Ther. 2004;26:1714–1727. - PubMed
-
- Bode KA, Donner MG, Leier I, Keppler D. Inhibition of transport across the hepatocyte canalicular membrane by the antibiotic fusidate. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002;64:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Boyd AE, Aguilar-Bryan L, Nelson DA. Molecular mechanisms of action of glyburide on the beta cell. Am. J. Med. 1990;89:3S–10S. - PubMed
-
- Gale EA. Lessons from the glitazones: a story of drug development. Lancet. 2001;357:1870–1875. - PubMed
-
- Gibbs TT, Russek SJ, Farb DH. Sulfated steroids as endogenous neuromodulators. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006;84:555–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

