Catalysis of lysine 48-specific ubiquitin chain assembly by residues in E2 and ubiquitin
- PMID: 20797627
- PMCID: PMC2929935
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.027
Catalysis of lysine 48-specific ubiquitin chain assembly by residues in E2 and ubiquitin
Abstract
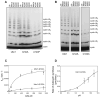
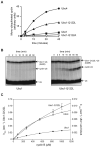
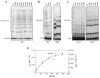
Protein ubiquitination is catalyzed by ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s) in collaboration with ubiquitin-protein ligases (E3s). This process depends on nucleophilic attack by a substrate lysine on a thioester bond linking the C terminus of ubiquitin to a cysteine in the E2 active site. Different E2 family members display specificity for lysines in distinct contexts. We addressed the mechanistic basis for this lysine selectivity in Ubc1, an E2 that catalyzes the ubiquitination of lysine 48 (K48) in ubiquitin, leading to the formation of K48-linked polyubiquitin chains. We identified a cluster of polar residues near the Ubc1 active site, as well as a residue in ubiquitin itself, that are required for catalysis of K48-specific ubiquitin ligation, but not for general activity toward other lysines. Our results suggest that the active site of Ubc1, as well as the surface of ubiquitin, contains specificity determinants that channel specific lysines to the central residues involved directly in catalysis.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bernier-Villamor V, Sampson DA, Matunis MJ, Lima CD. Structural basis for E2-mediated SUMO conjugation revealed by a complex between ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc9 and RanGAP1. Cell. 2002;108:345–356. - PubMed
-
- Carroll CW, Morgan DO. Enzymology of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex. Meth Enzymol. 2005;398:219–230. - PubMed
-
- Cook WJ, Jeffrey LC, Xu Y, Chau V. Tertiary structures of class I ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes are highly conserved: crystal structure of yeast Ubc4. Biochemistry. 1993;32:13809–13817. - PubMed
-
- DeLano WL. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System. Palo Alto, CA, USA: DeLano Scientific LLC; 2008. http://www.pymol.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

