A proteomic screen for nucleolar SUMO targets shows SUMOylation modulates the function of Nop5/Nop58
- PMID: 20797632
- PMCID: PMC2938476
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.025
A proteomic screen for nucleolar SUMO targets shows SUMOylation modulates the function of Nop5/Nop58
Abstract
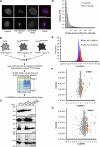
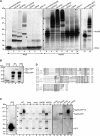
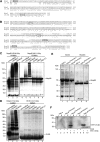
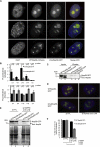
Posttranslational SUMO modification is an important mechanism of regulating protein function, especially in the cell nucleus. The nucleolus is the subnuclear organelle responsible for rRNA synthesis, processing, and assembly of the large and small ribosome subunits. Here, we have used SILAC-based quantitative proteomics to identify nucleolar SUMOylated proteins. This reveals a role for SUMOylation in the biogenesis and/or function of small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein complexes (snoRNPs) via the targeting of Nhp2 and Nop58. Using combined in vitro and in vivo approaches, both Nhp2 and Nop58 (also known as Nop5) are shown to be substrates for SUMOylation. Mutational analyses revealed the sites of modification on Nhp2 as K5, and on Nop58 as K467 and K497. Unlike Nop58 and Nhp2, the closely related Nop56 and 15.5K proteins appear not to be SUMO targets. SUMOylation is essential for high-affinity Nop58 binding to snoRNAs. This study provides direct evidence linking SUMO modification with snoRNP function.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A role for SUMOylation in snoRNP biogenesis revealed by quantitative proteomics.Nucleus. 2011 Jan-Feb;2(1):30-7. doi: 10.4161/nucl.2.1.14437. Nucleus. 2011. PMID: 21647297 Free PMC article.
-
The deubiquitinase USP36 promotes snoRNP group SUMOylation and is essential for ribosome biogenesis.EMBO Rep. 2021 Jun 4;22(6):e50684. doi: 10.15252/embr.202050684. Epub 2021 Apr 14. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33852194 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved stem II of the box C/D motif is essential for nucleolar localization and is required, along with the 15.5K protein, for the hierarchical assembly of the box C/D snoRNP.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;22(23):8342-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.23.8342-8352.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12417735 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics strategies to identify SUMO targets and acceptor sites: a survey of RNA-binding proteins SUMOylation.Neuromolecular Med. 2013 Dec;15(4):661-76. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8256-8. Epub 2013 Aug 25. Neuromolecular Med. 2013. PMID: 23979992 Review.
-
SUMO routes ribosome maturation.Nucleus. 2011 Nov-Dec;2(6):527-32. doi: 10.4161/nucl.2.6.17604. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Nucleus. 2011. PMID: 22064470 Review.
Cited by
-
SUMO conjugation regulates the activity of the Integrator complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Nov 28;50(21):12444-12461. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1055. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36454007 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-Mediated Regulation of Nuclear Functions and Signaling Processes.Mol Cell. 2018 Aug 2;71(3):409-418. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.027. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30075142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of nuclear bodies in gene expression and disease.Biology (Basel). 2013 Jul 9;2(3):976-1033. doi: 10.3390/biology2030976. Biology (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24040563 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like signaling networks.Chem Rev. 2011 Dec 14;111(12):7923-40. doi: 10.1021/cr200187e. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Chem Rev. 2011. PMID: 22004258 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Nutritional status modulates box C/D snoRNP biogenesis by regulated subcellular relocalization of the R2TP complex.Genome Biol. 2014 Jul 25;15(7):404. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0404-4. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 25060708 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen J.S., Lyon C.E., Fox A.H., Leung A.K., Lam Y.W., Steen H., Mann M., Lamond A.I. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr. Biol. 2002;12:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Boisvert F.M., van Koningsbruggen S., Navascues J., Lamond A.I. The multifunctional nucleolus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:574–585. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

