Long-term effects of prenatal omega-3 fatty acid intake on visual function in school-age children
- PMID: 20797725
- PMCID: PMC2992831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.06.056
Long-term effects of prenatal omega-3 fatty acid intake on visual function in school-age children
Abstract
Objective: To assess the long-term effect on visual development of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (n-3 PUFA) intake during gestation.
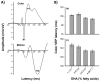
Study design: Using visual evoked potentials (VEPs), the long-term effects on visual development were evaluated in 136 school-age Inuit children exposed to high levels of n-3 PUFAs during gestation. VEP protocols using color and motion stimuli were used to assess parvocellular and magnocellular responses. Concentrations of the two major n-3 PUFAs (docosahexaenoic acid [DHA] and eicosapentaenoic acid [EPA]) were measured in umbilical cord and child plasma phospholipids, reflecting prenatal and postnatal exposure, respectively.
Results: After adjustment for confounders, cord plasma DHA level was found to be associated with shorter latencies of the N1 and P1 components of the color VEPs. No effects were found for current n-3 PUFA body burden or motion-onset VEPs.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates beneficial effects of DHA intake during gestation on visual system function at school age. DHA is particularly important for the early development and long-term function of the visual parvocellular pathway.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Jump DB, Clarke SD. Regulation of gene expression by dietary fat. Annu Rev Nutr. 1999;19:63–90. - PubMed
-
- McNamara RK, Carlson SE. Role of omega-3 fatty acids in brain development and function: potential implications for the pathogenesis and prevention of psychopathology. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2006;75(4-5):329–349. - PubMed
-
- Fliesler SJ, Anderson RE. Chemistry and metabolism of lipids in the vertebrate retina. Prog Lipid Res. 1983;22(2):79–131. - PubMed
-
- Kidd PM. Omega-3 DHA and EPA for cognition, behavior, and mood: clinical findings and structural-functional synergies with cell membrane phospholipids. Altern Med Rev. 2007;12(3):207–227. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GJ, Neuringer M, Lin DS, Connor WE. Can prenatal N-3 fatty acid deficiency be completely reversed after birth? Effects on retinal and brain biochemistry and visual function in rhesus monkeys. Pediatr Res. 2005;58(5):865–872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials