Fine-tuning of neuronal architecture requires two profilin isoforms
- PMID: 20798032
- PMCID: PMC2936622
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1004406107
Fine-tuning of neuronal architecture requires two profilin isoforms
Abstract
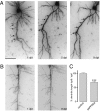
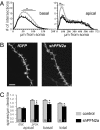
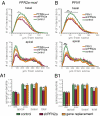
Two profilin isoforms (PFN1 and PFN2a) are expressed in the mammalian brain. Although profilins are essential for regulating actin dynamics in general, the specific role of these isoforms in neurons has remained elusive. We show that knockdown of the neuron-specific PFN2a results in a significant reduction in dendrite complexity and spine numbers of hippocampal neurons. Overexpression of PFN1 in PFN2a-deficient neurons prevents the loss of spines but does not restore dendritic complexity. Furthermore, we show that profilins are involved in differentially regulating actin dynamics downstream of the pan-neurotrophin receptor (p75(NTR)), a receptor engaged in modulating neuronal morphology. Overexpression of PFN2a restores the morphological changes in dendrites caused by p75(NTR) overexpression, whereas PFN1 restores the normal spine density. Our data assign specific functions to the two PFN isoforms, possibly attributable to different affinities for potent effectors also involved in actin dynamics, and suggest that they are important for the signal-dependent fine-tuning of neuronal architecture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuronal profilin isoforms are addressed by different signalling pathways.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034167. Epub 2012 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22470532 Free PMC article.
-
In birds, profilin-2a is ubiquitously expressed and contributes to actin-based motility.J Cell Sci. 2009 Apr 1;122(Pt 7):957-64. doi: 10.1242/jcs.041715. Epub 2009 Mar 3. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19258389
-
Neuronal profilins in health and disease: Relevance for spine plasticity and Fragile X syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 22;113(12):3365-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516697113. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26951674 Free PMC article.
-
Profilin Isoforms in Health and Disease - All the Same but Different.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 12;9:681122. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.681122. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34458253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The profile of profilins.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;159:131-49. doi: 10.1007/112_2007_704. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17682948 Review.
Cited by
-
Topological characterization of neuronal arbor morphology via sequence representation: II--global alignment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Jul 4;16(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0605-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26141505 Free PMC article.
-
Role of actin cytoskeleton in the organization and function of ionotropic glutamate receptors.Curr Res Struct Biol. 2021 Oct 14;3:277-289. doi: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2021.10.001. eCollection 2021. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 34766008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendrosomatic Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Hippocampal Neurons Regulates Axon Elongation.J Neurosci. 2015 Dec 9;35(49):16126-41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1360-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26658865 Free PMC article.
-
NCAM regulates temporal specification of neural progenitor cells via profilin2 during corticogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2020 Jan 6;219(1):e201902164. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201902164. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31816056 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying How Staining Methods Bias Measurements of Neuron Morphologies.Front Neuroinform. 2019 May 21;13:36. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2019.00036. eCollection 2019. Front Neuroinform. 2019. PMID: 31191283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carlsson L, Nyström LE, Sundkvist I, Markey F, Lindberg U. Actin polymerizability is influenced by profilin, a low molecular weight protein in non-muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1977;115:465–483. - PubMed
-
- Jockusch BM, Murk K, Rothkegel M. The profile of profilins. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;159:131–149. - PubMed
-
- Neuhoff H, et al. The actin-binding protein profilin I is localized at synaptic sites in an activity-regulated manner. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;21:15–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

