Defective membrane expression of the Na(+)-HCO(3)(-) cotransporter NBCe1 is associated with familial migraine
- PMID: 20798035
- PMCID: PMC2936614
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1008705107
Defective membrane expression of the Na(+)-HCO(3)(-) cotransporter NBCe1 is associated with familial migraine
Abstract
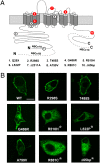
Homozygous mutations in SLC4A4, encoding the electrogenic Na(+)-HCO(3)(-) cotransporter NBCe1, have been known to cause proximal renal tubular acidosis (pRTA) and ocular abnormalities. In this study, we report two sisters with pRTA, ocular abnormalities, and hemiplegic migraine. Genetic analysis ruled out pathological mutations in the known genes for familial hemiplegic migraine, but identified a homozygous 65-bp deletion (Delta65bp) in the C terminus of NBCe1, corresponding to the codon change S982NfsX4. Several heterozygous members of this family also presented glaucoma and migraine with or without aura. Despite the normal electrogenic activity in Xenopus oocytes, the Delta65bp mutant showed almost no transport activity due to a predominant cytosolic retention in mammalian cells. Furthermore, coexpression experiments uncovered a dominant negative effect of the mutant through hetero-oligomer formation with wild-type NBCe1. Among other pRTA pedigrees with different NBCe1 mutations, we identified four additional homozygous patients with migraine. The immunohistological and functional analyses of these mutants demonstrate that the near total loss of NBCe1 activity in astrocytes can cause migraine potentially through dysregulation of synaptic pH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lipton RB, et al. Migraine in the United States: Epidemiology and patterns of health care use. Neurology. 2002;58:885–894. - PubMed
-
- Ophoff RA, et al. Familial hemiplegic migraine and episodic ataxia type-2 are caused by mutations in the Ca2+ channel gene CACNL1A4. Cell. 1996;87:543–552. - PubMed
-
- De Fusco M, et al. Haploinsufficiency of ATP1A2 encoding the Na+/K+ pump alpha2 subunit associated with familial hemiplegic migraine type 2. Nat Genet. 2003;33:192–196. - PubMed
-
- Dichgans M, et al. Mutation in the neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel SCN1A in familial hemiplegic migraine. Lancet. 2005;366:371–377. - PubMed
-
- Pietrobon D, Striessnig J. Neurobiology of migraine. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:386–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

