H-NS forms a superhelical protein scaffold for DNA condensation
- PMID: 20798056
- PMCID: PMC2936596
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1006966107
H-NS forms a superhelical protein scaffold for DNA condensation
Abstract
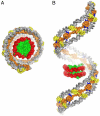
The histone-like nucleoid structuring (H-NS) protein plays a fundamental role in DNA condensation and is a key regulator of enterobacterial gene expression in response to changes in osmolarity, pH, and temperature. The protein is capable of high-order self-association via interactions of its oligomerization domain. Using crystallography, we have solved the structure of this complete domain in an oligomerized state. The observed superhelical structure establishes a mechanism for the self-association of H-NS via both an N-terminal antiparallel coiled-coil and a second, hitherto unidentified, helix-turn-helix dimerization interface at the C-terminal end of the oligomerization domain. The helical scaffold suggests the formation of a H-NS:plectonemic DNA nucleoprotein complex that is capable of explaining published biophysical and functional data, and establishes a unifying structural basis for coordinating the DNA packaging and transcription repression functions of H-NS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hommais F, et al. Large-scale monitoring of pleiotropic regulation of gene expression by the prokaryotic nucleoid-associated protein, H-NS. Mol Microbiol. 2001;40:20–36. - PubMed
-
- Hulton CS, et al. Histone-like protein H1 (H-NS), DNA supercoiling, and gene expression in bacteria. Cell. 1990;63:631–642. - PubMed
-
- Mukerji M, Mahadevan S. Characterization of the negative elements involved in silencing the bgl operon of Escherichia coli: possible roles for DNA gyrase, H-NS, and CRP-cAMP in regulation. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24:617–627. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

