Assembly of Q{beta} viral RNA polymerase with host translational elongation factors EF-Tu and -Ts
- PMID: 20798060
- PMCID: PMC2936634
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1006559107
Assembly of Q{beta} viral RNA polymerase with host translational elongation factors EF-Tu and -Ts
Abstract
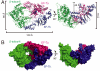
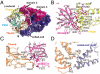
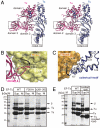
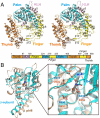
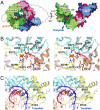
Replication and transcription of viral RNA genomes rely on host-donated proteins. Qbeta virus infects Escherichia coli and replicates and transcribes its own genomic RNA by Qbeta replicase. Qbeta replicase requires the virus-encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (beta-subunit), and the host-donated translational elongation factors EF-Tu and -Ts, as active core subunits for its RNA polymerization activity. Here, we present the crystal structure of the core Qbeta replicase, comprising the beta-subunit, EF-Tu and -Ts. The beta-subunit has a right-handed structure, and the EF-Tu:Ts binary complex maintains the structure of the catalytic core crevasse of the beta-subunit through hydrophobic interactions, between the finger and thumb domains of the beta-subunit and domain-2 of EF-Tu and the coiled-coil motif of EF-Ts, respectively. These hydrophobic interactions are required for the expression and assembly of the Qbeta replicase complex. Thus, EF-Tu and -Ts have chaperone-like functions in the maintenance of the structure of the active Qbeta replicase. Modeling of the template RNA and the growing RNA in the catalytic site of the Qbeta replicase structure also suggests that structural changes of the RNAs and EF-Tu:Ts should accompany processive RNA polymerization and that EF-Tu:Ts in the Qbeta replicase could function to modulate the RNA folding and structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular basis for RNA polymerization by Qβ replicase.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 15;19(2):229-37. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2204. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22245970
-
Reconstitution of Qbeta RNA replicase from a covalently bonded elongation factor Tu-Ts complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1131-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1131. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976. PMID: 1063392 Free PMC article.
-
Structures and functions of Qβ replicase: translation factors beyond protein synthesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Sep 2;15(9):15552-70. doi: 10.3390/ijms150915552. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25184952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qbeta-phage resistance by deletion of the coiled-coil motif in elongation factor Ts.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 16;279(3):1878-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306605200. Epub 2003 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14583631
-
Elongation in bacterial protein biosynthesis.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1996 Aug;7(4):369-75. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(96)80110-8. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1996. PMID: 8768893 Review.
Cited by
-
A design principle for a single-stranded RNA genome that replicates with less double-strand formation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Sep 18;43(16):8033-43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv742. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26202975 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-free expression of RNA encoded genes using MS2 replicase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Nov 18;47(20):10956-10967. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz817. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31566241 Free PMC article.
-
The Single-Stranded RNA Bacteriophage Qβ Adapts Rapidly to High Temperatures: An Evolution Experiment.Viruses. 2020 Jun 12;12(6):638. doi: 10.3390/v12060638. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32545482 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of the eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A with the 5'UTR of HIV-1 genomic RNA is important for reverse transcription.Virol J. 2015 Aug 6;12:118. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0337-x. Virol J. 2015. PMID: 26242867 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Psychrophilic vs. Mesophilic Bacterial Species Reveals Different Strategies to Achieve Temperature Adaptation.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 3;13:841359. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.841359. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35591995 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

