Functional interactions between membrane-bound transporters and membranes
- PMID: 20798065
- PMCID: PMC2936589
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1006109107
Functional interactions between membrane-bound transporters and membranes
Abstract
One key role of many cellular membranes is to hold a transmembrane electrochemical ion gradient that stores free energy, which is used, for example, to generate ATP or to drive transmembrane transport processes. In mitochondria and many bacteria, the gradient is maintained by proton-transport proteins that are part of the respiratory (electron-transport) chain. Even though our understanding of the structure and function of these proteins has increased significantly, very little is known about the specific role of functional protein-membrane and membrane-mediated protein-protein interactions. Here, we have investigated the effect of membrane incorporation on proton-transfer reactions within the membrane-bound proton pump cytochrome c oxidase. The results show that the membrane acts to accelerate proton transfer into the enzyme's catalytic site and indicate that the intramolecular proton pathway is wired via specific amino acid residues to the two-dimensional space defined by the membrane surface. We conclude that the membrane not only acts as a passive barrier insulating the interior of the cell from the exterior solution, but also as a component of the energy-conversion machinery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

 ) and thin arrows (
) and thin arrows ( ) indicate rapid proton transfer in the membrane-reconstituted CytcO and slower proton transfer in detergent-solubilized CytcO, respectively. The arrow within CytcO indicates proton transfer via LysI362 within the K proton pathway.
) indicate rapid proton transfer in the membrane-reconstituted CytcO and slower proton transfer in detergent-solubilized CytcO, respectively. The arrow within CytcO indicates proton transfer via LysI362 within the K proton pathway.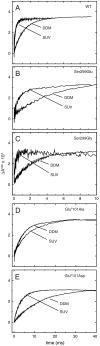
References
-
- Kung C. A possible unifying principle for mechanosensation. Nature. 2005;436:647–654. - PubMed
-
- Lee AG. How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. BBA-Biomembranes. 2004;1666:62–87. - PubMed
-
- Williams RJP. The multifarious couplings of energy transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978;505:1–44. - PubMed
-
- Mulkidjanian AY, Heberle J, Cherepanov DA. Protons @ interfaces: Implications for biological energy conversion. BBA-Bioenergetics. 2006;1757:913–930. - PubMed
-
- Heberle J. Proton transfer reactions across bacteriorhodopsin and along the membrane. BBA-Bioenergetics. 2000;1458:135–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

