Quality of life in hormone receptor-positive HER-2+ metastatic breast cancer patients during treatment with letrozole alone or in combination with lapatinib
- PMID: 20798196
- PMCID: PMC3228031
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0012
Quality of life in hormone receptor-positive HER-2+ metastatic breast cancer patients during treatment with letrozole alone or in combination with lapatinib
Abstract
Background: A phase III trial compared lapatinib plus letrozole (L + Let) with letrozole plus placebo (Let) as first-line therapy for hormone receptor (HR)(+) metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients. The primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) in patients whose tumors were human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)-2(+) was significantly longer for L + Let than for Let (8.2 months versus 3 months; p = .019). This analysis focuses on quality of life (QOL) in the HER-2(+) population.
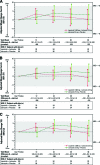
Methods: QOL was assessed at screening, every 12 weeks, and at withdrawal using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast (FACT-B). Changes from baseline were analyzed and the proportions of patients achieving minimally important differences in QOL scores were compared. Additional exploratory analyses evaluated how QOL changes reflected tumor progression status.
Results: Among the 1,286 patients randomized, 219 had HER-2(+) tumors. Baseline QOL scores were comparable in the two arms. Mean changes in QOL scores were generally stable over time for patients who stayed on study. The average change from baseline on the FACT-B total score in both arms was positive at all scheduled visits through week 48. There was no significant difference between the two treatment arms in the percentage of QOL responders.
Conclusion: The addition of lapatinib to letrozole led to a significantly longer PFS interval while maintaining QOL during treatment, when compared with letrozole alone, thus confirming the clinical benefit of the combination therapy in the HR(+) HER-2(+) MBC patient population. This all oral regimen provides an effective option in this patient population, delaying the need for chemotherapy and its accompanying side effects.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00073528.
Conflict of interest statement
The article discusses results from the clinical trial EGF30008 that studied the combination of letrozole plus lapatinib in metastatic breast cancer treatment.
The content of this article has been reviewed by independent peer reviewers to ensure that it is balanced, objective, and free from commercial bias. No financial relationships relevant to the content of this article have been disclosed by the independent peer reviewers.
Figures


References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Lipton A, Ali SM, Leitzel K, et al. Serum HER-2/neu and response to the aromatase inhibitor letrozole versus tamoxifen. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1967–1972. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson RI, Gee JMW, Harper ME. EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(suppl 4):S9–S15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

