Cubilin is essential for albumin reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule
- PMID: 20798259
- PMCID: PMC3014001
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010050492
Cubilin is essential for albumin reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule
Abstract
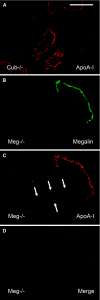
Receptor-mediated endocytosis is responsible for protein reabsorption in the proximal tubule. This process involves two interacting receptors, megalin and cubilin, which form a complex with amnionless. Whether these proteins function in parallel or as part of an integrated system is not well understood. Here, we report the renal effects of genetic ablation of cubilin, with or without concomitant ablation of megalin, using a conditional Cre-loxP system. We observed that proximal tubule cells did not localize amnionless to the plasma membrane in the absence of cubilin, indicating a mutual dependency of cubilin and amnionless to form a functional membrane receptor complex. The cubilin-amnionless complex mediated internalization of intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 complexes, but megalin considerably increased the uptake. Furthermore, cubilin-deficient mice exhibited markedly decreased uptake of albumin by proximal tubule cells and resultant albuminuria. Inactivation of both megalin and cubilin did not increase albuminuria, indicating that the main role of megalin in albumin reabsorption is to drive the internalization of cubilin-albumin complexes. In contrast, cubulin deficiency did not affect urinary tubular uptake or excretion of vitamin D-binding protein (DBP), which binds cubilin and megalin. In addition, we observed cubilin-independent reabsorption of the "specific" cubilin ligands transferrin, CC16, and apoA-I, suggesting a role for megalin and perhaps other receptors in their reabsorption. In summary, with regard to albumin, cubilin is essential for its reabsorption by proximal tubule cells, and megalin drives internalization of cubilin-albumin complexes. These genetic models will allow further analysis of protein trafficking in the progression of proteinuric renal diseases.
Figures

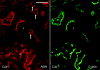
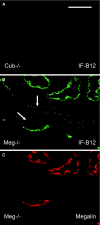
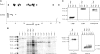
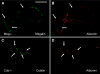
Comment in
-
Tubular reabsorption of albumin: it's all about cubilin.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Nov;21(11):1810-2. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010090984. Epub 2010 Oct 14. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20947627 No abstract available.
References
-
- Christensen EI, Verroust PJ, Nielsen R: Receptor-mediated endocytosis in renal proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch 458: 1039–1048, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Maack T, Park CH, Camargo MJF: Renal filtration, transport and metabolism of proteins. In: The Kidney, 2nd Ed., edited by Seldin DW, Giebisch G. New York, Raven Press, 1992, pp 3005–3038
-
- Moestrup SK, Kozyraki R, Kristiansen M, Kaysen JH, Rasmussen HH, Brault D, Pontillon F, Goda FO, Christensen EI, Hammond TG, Verroust PJ: The intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 receptor and target of teratogenic antibodies is a megalin-binding peripheral membrane protein with homology to developmental proteins. J Biol Chem 273: 5235–5242, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Birn H, Verroust PJ, Nexø E, Hager H, Jacobsen C, Christensen EI, Moestrup SK: Characterization of an epithelial approximately 460-kDa protein that facilitates endocytosis of intrinsic factor-vitamin B12 and binds receptor-associated protein. J Biol Chem 272: 26497–26504, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

