G-quadruplex structures in RNA stimulate mitochondrial transcription termination and primer formation
- PMID: 20798345
- PMCID: PMC2941323
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1006026107
G-quadruplex structures in RNA stimulate mitochondrial transcription termination and primer formation
Abstract
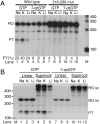
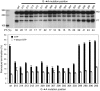
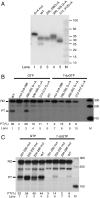
The human mitochondrial transcription machinery generates the primers required for initiation of leading-strand DNA replication. According to one model, the 3' end of the primer is defined by transcription termination at conserved sequence block II (CSB II) in the mitochondrial DNA control region. We here demonstrate that this site-specific termination event is caused by G-quadruplex structures formed in nascent RNA upon transcription of CSB II. We also demonstrate that a poly-dT stretch downstream of CSB II has a modest stimulatory effect on the termination efficiency. The mechanism is reminiscent of Rho-independent transcription termination in prokaryotes, with the exception that a G-quadruplex structure replaces the hairpin loop formed in bacterial mRNA during transcription of terminator sequences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

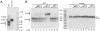
References
-
- Shadel GS, Clayton DA. Mitochondrial DNA maintenance in vertebrates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997;66:409–435. - PubMed
-
- Clayton DA. Replication and transcription of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:453–478. - PubMed
-
- Ojala D, Montoya J, Attardi G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature. 1981;290:470–474. - PubMed
-
- Pham XH, et al. Conserved sequence box II directs transcription termination and primer formation in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24647–24652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

