Ocular syphilis among HIV-infected patients: a systematic analysis of the literature
- PMID: 20798396
- PMCID: PMC3103105
- DOI: 10.1136/sti.2010.043042
Ocular syphilis among HIV-infected patients: a systematic analysis of the literature
Abstract
Background: Ocular syphilis among HIV-infected patients continues to be a problem in the highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) era. However, outside of case reports or small case series, little is known about the clinical, laboratory, and treatment outcomes of these patients. Objective To examine the literature on HIV-infected patients and determine the results of treatment.
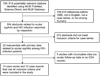
Methods: Systematic review of cases series and case reports among HIV-infected individuals with ocular syphilis. Reviews, languages other than English and pre-1980 reports were excluded. The effect of CD4 count and virological suppression on clinical manifestations and diagnostic laboratory values was evaluated.
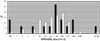
Results: A total of 101 HIV-infected individuals in case series and case reports were identified. Ocular syphilis led to the HIV diagnosis in 52% of cases, including patients with CD4 count >200 cells/mm(3). Posterior uveitis was significantly more common in individuals with CD4 count <200 cells/mm(3) (p = 0.002). Three patients with confirmed ocular syphilis had negative non-treponemal tests. Ninety-seven per cent of patients with visual impairment improved following intravenous penicillin or ceftriaxone.
Conclusions: Non-treponemal tests may be negative in HIV-infected patients with ocular syphilis. Ocular syphilis remains an important clinical manifestation that can lead to initial HIV diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Kedhar SR, Jabs DA. Cytomegalovirus retinitis in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Herpes. 2007;14:66–71. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Lopez JJ, Guerrero ML, Lujan R, et al. Factors determining serologic response to treatment in patients with syphilis. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:1505–1511. - PubMed
-
- Berry CD, Hooton TM, Collier AC, et al. Neurologic relapse after benzathine penicillin therapy for secondary syphilis in a patient with HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:1587–1589. - PubMed
-
- Booth J, Rodger A, Singh J, et al. Syphilitic panuveitis with retinal necrosis in an HIV positive man confirmed by treponema pallidum PCR. J Infect. 2009;59:373–375. - PubMed
-
- Carter JB, Hamill RJ, Matoba AY. Bilateral syphilitic optic neuritis in a patient with a positive test for HIV. Case report. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987;105:1485–1486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
