Calcium sensing receptor mutations implicated in pancreatitis and idiopathic epilepsy syndrome disrupt an arginine-rich retention motif
- PMID: 20798521
- PMCID: PMC3709174
- DOI: 10.1159/000320560
Calcium sensing receptor mutations implicated in pancreatitis and idiopathic epilepsy syndrome disrupt an arginine-rich retention motif
Abstract
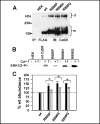
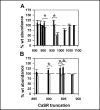
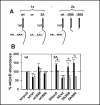
Calcium sensing receptor (CaSR) mutations implicated in familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia, pancreatitis and idiopathic epilepsy syndrome map to an extended arginine-rich region in the proximal carboxyl terminus. Arginine-rich motifs mediate endoplasmic reticulum retention and/or retrieval of multisubunit proteins so we asked whether these mutations, R886P, R896H or R898Q, altered CaSR targeting to the plasma membrane. Targeting was enhanced by all three mutations, and Ca(2+)-stimulated ERK1/2 phosphorylation was increased for R896H and R898Q. To define the role of the extended arginine-rich region in CaSR trafficking, we independently determined the contributions of R890/R891 and/or R896/K897/R898 motifs by mutation to alanine. Disruption of the motif(s) significantly increased surface expression and function relative to wt CaSR. The arginine-rich region is flanked by phosphorylation sites at S892 (protein kinase C) and S899 (protein kinase A). The phosphorylation state of S899 regulated recognition of the arginine-rich region; S899D showed increased surface localization. CaSR assembles in the endoplasmic reticulum as a covalent disulfide-linked dimer and we determined whether retention requires the presence of arginine-rich regions in both subunits. A single arginine-rich region within the dimer was sufficient to confer intracellular retention comparable to wt CaSR. We have identified an extended arginine-rich region in the proximal carboxyl terminus of CaSR (residues R890 - R898) which fosters intracellular retention of CaSR and is regulated by phosphorylation. Mutation(s) identified in chronic pancreatitis and idiopathic epilepsy syndrome therefore increase plasma membrane targeting of CaSR, likely contributing to the altered Ca(2+) signaling characteristic of these diseases.
Copyright 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Calcium signaling regulates trafficking of familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) mutants of the calcium sensing receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Dec;26(12):2081-91. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1232. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 23077345 Free PMC article.
-
14-3-3 Proteins Buffer Intracellular Calcium Sensing Receptors to Constrain Signaling.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0136702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136702. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26317416 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-sensing receptor biosynthesis includes a cotranslational conformational checkpoint and endoplasmic reticulum retention.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 25;285(26):19854-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.124792. Epub 2010 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20421307 Free PMC article.
-
The calcium sensing receptor life cycle: trafficking, cell surface expression, and degradation.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jun;27(3):303-13. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 Apr 19. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23856261 Review.
-
Insights into calcium-sensing receptor trafficking and biased signalling by studies of calcium homeostasis.J Mol Endocrinol. 2018 Jul;61(1):R1-R12. doi: 10.1530/JME-18-0049. Epub 2018 Mar 29. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29599414 Review.
Cited by
-
Minireview: the intimate link between calcium sensing receptor trafficking and signaling: implications for disorders of calcium homeostasis.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Sep;26(9):1482-95. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1370. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22745192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large putative PEST-like sequence motif at the carboxyl tail of human calcium receptor directs lysosomal degradation and regulates cell surface receptor level.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 3;287(6):4165-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.271528. Epub 2011 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22158862 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium signaling regulates trafficking of familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) mutants of the calcium sensing receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Dec;26(12):2081-91. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1232. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 23077345 Free PMC article.
-
14-3-3 Proteins Buffer Intracellular Calcium Sensing Receptors to Constrain Signaling.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 28;10(8):e0136702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136702. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26317416 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CVIII. Calcium-Sensing Receptor Nomenclature, Pharmacology, and Function.Pharmacol Rev. 2020 Jul;72(3):558-604. doi: 10.1124/pr.119.018531. Pharmacol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32467152 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brown EM. The calcium-sensing receptor: physiology, pathophysiology and CaR-based therapeutics. Subcell Biochem. 2007;45:139–167. - PubMed
-
- Bruce JI, Yang X, Ferguson CJ, Elliott AC, Steward MC, Case RM, Riccardi D. Molecular and functional identification of a Ca2+ (polyvalent cation)-sensing receptor in rat pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:20561–20568. - PubMed
-
- Chen JM, Ferec C. Chronic pancreatitis: genetics and pathogenesis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2009;10:63–87. - PubMed
-
- Whitcomb DC. Genetic aspects of pancreatitis. Annu Rev Med. 2010;61:413–424. - PubMed
-
- Muddana V, Lamb J, Greer JB, Elinoff B, Hawes RH, Cotton PB, Anderson MA, Slivka A, Whitcomb DC. Association between calcium sensing receptor gene polymorphisms and chronic pancreatitis in a US population: role of serine protease inhibitor Kazal 1type and alcohol. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:4486–4491. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
