Liquid drugs and high dead space syringes may keep HIV and HCV prevalence high - a comparison of Hungary and Lithuania
- PMID: 20798543
- PMCID: PMC2969108
- DOI: 10.1159/000320287
Liquid drugs and high dead space syringes may keep HIV and HCV prevalence high - a comparison of Hungary and Lithuania
Abstract
Despitevery similar political, drug policy and HIV prevention backgrounds, HIV and HCV prevalence is considerably different in Hungary (low HIV and moderate HCV prevalence) and Lithuania (high HCV and moderate HIV prevalence). Wecompared the drug use profile of Hungarian (n = 215) and Lithuanian (n = 300) injecting drug users (IDUs). Overall, compared with IDUs in Hungary, IDUs in Lithuania often injected opiates purchased in liquid form ('shirka'), used and shared 2-piece syringes (vs. 1-piece syringes) disproportionately more often, were less likely to acquire their syringes from legal sources and had significantly more experience with injected and less experience with non-injected drugs. It may not be liquid drugs per se that contribute to a higher prevalence of HCV and/or HIV, but it is probably factors associated with the injecting of liquid drugs, such as the wide-spread use and sharing of potentially contaminated 2-piece syringes acquired often from non-legal sources, and syringe-mediated drug sharing with 2-piece syringes. Scaling up substitution therapy, especially heroin replacement, combined with reducing the supply of liquid drugs may decrease the prevalence of high-risk injecting behaviours related to the injecting of liquid drugs and drug injecting-related infections among IDUs in Lithuania.
Copyright © 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
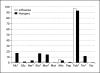
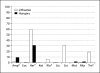
Similar articles
-
The association of syringe type and syringe cleaning with HCV infection among IDUs in Budapest, Hungary.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009 Mar 1;100(3):240-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.10.014. Epub 2008 Dec 5. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2009. PMID: 19058925 Free PMC article.
-
Greater drug injecting risk for HIV, HBV, and HCV infection in a city where syringe exchange and pharmacy syringe distribution are illegal.J Urban Health. 2008 May;85(3):309-22. doi: 10.1007/s11524-008-9271-1. Epub 2008 Mar 14. J Urban Health. 2008. PMID: 18340537 Free PMC article.
-
Infection disclosure in the injecting dyads of Hungarian and Lithuanian injecting drug users who self-reported being infected with hepatitis C virus or human immunodeficiency virus.Scand J Infect Dis. 2011 Jan;43(1):32-42. doi: 10.3109/00365548.2010.513064. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Scand J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 20840002 Free PMC article.
-
[Epidemiology of hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus infections among injecting drug users in Hungary--what's next?].Orv Hetil. 2010 Mar 7;151(10):365-71. doi: 10.1556/OH.2010.28821. Orv Hetil. 2010. PMID: 20178967 Review. Hungarian.
-
Integrating multiple programme and policy approaches to hepatitis C prevention and care for injection drug users: a comprehensive approach.Int J Drug Policy. 2007 Oct;18(5):417-25. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2007.01.013. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Int J Drug Policy. 2007. PMID: 17854731 Review.
Cited by
-
HIV seroprevalence in five key populations in Europe: a systematic literature review, 2009 to 2019.Euro Surveill. 2021 Nov;26(47):2100044. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.47.2100044. Euro Surveill. 2021. PMID: 34823636 Free PMC article.
-
Co-design of harm reduction materials for people who inject drugs to implement research findings.Harm Reduct J. 2019 Jun 7;16(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12954-019-0300-z. Harm Reduct J. 2019. PMID: 31174536 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-HCV prevalence in the general population of Lithuania.Med Sci Monit. 2012 Mar;18(3):PH28-35. doi: 10.12659/msm.882511. Med Sci Monit. 2012. PMID: 22367136 Free PMC article.
-
HIV among people who inject drugs in Central and Eastern Europe and Central Asia: a systematic review with implications for policy.BMJ Open. 2012 Oct 18;2(5):e001465. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001465. Print 2012. BMJ Open. 2012. PMID: 23087014 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with perceived ease of access to syringes in Appalachian North Carolina.J Rural Health. 2023 Jan;39(1):212-222. doi: 10.1111/jrh.12698. Epub 2022 Jul 12. J Rural Health. 2023. PMID: 35819251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wikipedia. Hungary. 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hungary (accessed November 20, 2009).
-
- Wikipedia. Lithuania. 2009. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lithuania (accessed November 20, 2009).
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction: HIV infections newly diagnosed in injecting drug users, by year of report from 1992 to 2007, (a) cases per million population, (b) number of cases and (c) population sizes. Statistical Bulletin 2009. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/stats09/inftab104
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction: Prevalence of HIV infection among injecting drug users in the EU, 2007 or most recent year available – summary table by country. Statistical Bulletin 2009. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/stats09/inftab1
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

