Kung fu training improves physical fitness measures in overweight/obese adolescents: the "martial fitness" study
- PMID: 20798764
- PMCID: PMC2925099
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/672751
Kung fu training improves physical fitness measures in overweight/obese adolescents: the "martial fitness" study
Abstract
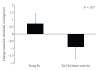
Aim. To examine the efficacy of a six-month Kung Fu (KF) program on physical fitness in overweight/obese adolescents. Methods. Subjects were randomly assigned to the KF or sham exercise (Tai Chi, TC) control group. Physical measurements in cardiovascular fitness and muscle fitness occurred at baseline and after 6 months of training thrice weekly. Results. Twenty subjects were recruited. One subject was lost to follow-up, although overall compliance to the training sessions was 46.7 +/- 27.8%. At follow-up, the cohort improved in absolute upper (P = .002) and lower (P = .04) body strength, and upper body muscle endurance (P = .02), without group differences. KF training resulted in significantly greater improvements in submaximal cardiovascular fitness (P = .03), lower body muscle endurance (P = .28; significant 95% CI: 0.37-2.49), and upper body muscle velocity (P = .03) relative to TC training. Conclusions. This short-term KF program improved submaximal cardiovascular fitness, lower body muscle endurance, and muscle velocity, in overweight/obese adolescents with very low baseline fitness.
Figures
References
-
- Swallen KC, Reither EN, Haas SA, Meier AM. Overweight, obesity, and health-related quality of life among adolescents: the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Pediatrics. 2005;115(2):340–347. - PubMed
-
- Pender JR, Pories WJ. Epidemiology of obesity in the United States. Gastroenterology Clinics of North America. 2005;34(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Zanconato S, Baraldi E, Santuz P, et al. Gas exchange during exercise in obese children. European Journal of Pediatrics. 1989;148(7):614–617. - PubMed
-
- Reybrouck T, Mertens L, Schepers D, Vinckx J, Gewillig M. Assessment of cardiorespiratory exercise function in obese children and adolescents by body mass-independent parameters. European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology. 1997;75(6):478–483. - PubMed
-
- Zoico E, Di Francesco V, Guralnik JM, et al. Physical disability and muscular strength in relation to obesity and different body composition indexes in a sample of healthy elderly women. International Journal of Obesity & Related Metabolic Disorders. 2004;28(2):234–241. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources