Cellular machinery to fuse antimicrobial autophagosome with lysosome
- PMID: 20798834
- PMCID: PMC2928326
- DOI: 10.4161/cib.3.4.12030
Cellular machinery to fuse antimicrobial autophagosome with lysosome
Abstract
Autophagy is an intracellular bulk degradation/recycling system that turns over cellular constituents and also functions to degrade intracellular foreign microbial invaders by a process termed xenophagy (antimicrobial autophagy). We previously showed that intracellular group A Streptococcus (GAS) organisms are captured by xenophagosomes, then degraded following fusion with lysosomes. Very recently, we analyzed the molecular mechanism underlying xenophagosome/lysosome fusion and found that endocytic soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) were involved. Knockdown of the combinational SNARE proteins Vti1b and VAMP8 with siRNAs disturbed autophagic fusion with lysosomes, and cellular bactericidal efficiency was significantly diminished. Furthermore, knockdown of those SNAREs inhibited the fusion of canonical autophagosomes with lysosomes. In addition, important findings showed that Vti1b is derived from autophagic compartments, whereas VAMP8 originates from lysosomes. Together, these results strongly suggest that SNARE proteins Vti1b and VAMP8 mediate the fusion of antimicrobial and canonical autophagosomes with lysosomes, an essential event for autophagic degradation.
Keywords: SNARE; VAMP8; Vti1b; autophagy; xenophagy.
Figures
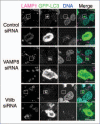
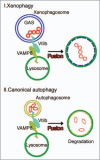
Comment on
-
Combinational soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor proteins VAMP8 and Vti1b mediate fusion of antimicrobial and canonical autophagosomes with lysosomes.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 15;21(6):1001-10. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0693. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20089838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cossart P, Sansonetti PJ. Bacterial invasion: the paradigms of enteroinvasive pathogens. Science. 2004;304:242–248. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimori T. Autophagy: a regulated bulk degradation process inside cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;313:453–458. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimori T, Amano A. Group A Streptococcus. A loser in the battle with autophagy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;335:217–226. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa I, Amano A, Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Yamaguchi H, Kamimoto T, et al. Autophagy defends cells against invading group A Streptococcus. Science. 2004;306:1037–1040. - PubMed
-
- Hamasaki M, Yoshimori T. Where do they come from? Insights into autophagosome formation. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:1296–1301. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
