Selective Incision of the alpha-N-Methyl-Formamidopyrimidine Anomer by Escherichia coli Endonuclease IV
- PMID: 20798848
- PMCID: PMC2925382
- DOI: 10.4061/2010/850234
Selective Incision of the alpha-N-Methyl-Formamidopyrimidine Anomer by Escherichia coli Endonuclease IV
Abstract
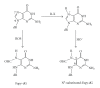
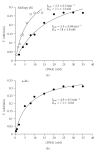
Formamidopyrimidines (Fapy) lesions result from ring opening of the imidazole portion of purines. Fapy lesions can isomerize from the natural beta-anomeric stereochemistry to the alpha-configuration. We have unambiguously demonstrated that the alpha-methyl-Fapy-dG (MeFapy-dG) lesion is a substrate for Escherichia coli Endonuclease IV (Endo IV). Treatment of a MeFapy-dG-containing 24 mer duplex with Endo IV resulted in 36-40% incision. The catalytic efficiency of the incision was comparable to that of alpha-dG in the same duplex sequence. The alpha- and beta-MeFapy-dG anomers equilibrate to ~21 : 79 ratio over ~3 days. Related studies with a duplex containing the alpha-Fapy-dG lesion derived from aflatoxin B(1) epoxide (alpha-AFB-Fapy-dG) showed only low levels of incision. It is hypothesized that the steric bulk of the aflatoxin moiety interferes with the binding of the substrate to Endo IV and the incision chemistry.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Probing the configurations of formamidopyrimidine lesions Fapy.dA and Fapy.dG in DNA using endonuclease IV.Biochemistry. 2004 Oct 26;43(42):13397-403. doi: 10.1021/bi049035s. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15491146
-
Structural perturbations induced by the alpha-anomer of the aflatoxin B(1) formamidopyrimidine adduct in duplex and single-strand DNA.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Nov 11;131(44):16096-107. doi: 10.1021/ja902052v. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19831353 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of N5-substituted formamidopyrimidine DNA adducts by DNA glycosylases NEIL1 and NEIL3.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Jan;73:49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 30448017 Free PMC article.
-
The formamidopyrimidines: purine lesions formed in competition with 8-oxopurines from oxidative stress.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Apr 17;45(4):588-97. doi: 10.1021/ar2002182. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22077696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imidazole ring-opened DNA purines and their biological significance.J Biochem Mol Biol. 2003 Jan 31;36(1):12-9. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2003.36.1.012. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12542970 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutagenic spectra arising from replication bypass of the 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-N(5)-methyl formamidopyrimidine adduct in primate cells.Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jul 15;26(7):1108-14. doi: 10.1021/tx4001495. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23763662 Free PMC article.
-
Highly mutagenic exocyclic DNA adducts are substrates for the human nucleotide incision repair pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051776. Epub 2012 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251620 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Biology of N5-Substituted Formamidopyrimidine DNA Adducts.Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 Jan 17;30(1):434-452. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00392. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27959490 Free PMC article.
-
Replication of the 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-N(5)-(methyl)-formamidopyrimidine (MeFapy-dGuo) adduct by eukaryotic DNA polymerases.Chem Res Toxicol. 2012 Aug 20;25(8):1652-61. doi: 10.1021/tx300113e. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22721435 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Active-Site Plasticity in Damaged-Nucleotide Recognition by Human Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease APE1.Molecules. 2020 Aug 28;25(17):3940. doi: 10.3390/molecules25173940. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32872297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenberg MM. In vitro and in vivo effects of oxidative damage to deoxyguanosine. Biochemical Society Transactions. 2004;32(1):46–50. - PubMed
-
- Pluskota-Karwatka D. Modifications of nucleosides by endogenous mutagens-DNA adducts arising from cellular processes. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2008;36(4):198–213. - PubMed
-
- Dizdaroglu M, Kirkali G, Jaruga P. Formamidopyrimidines in DNA: mechanisms of formation, repair, and biological effects. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2008;45(12):1610–1621. - PubMed
-
- Tudek B. Imidazole ring-opened DNA purines and their biological significance. Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2003;36(1):12–19. - PubMed
-
- Gates KS, Nooner T, Dutta S. Biologically relevant chemical reactions of N7-alkylguanine residues in DNA. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 2004;17(7):839–856. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

