Polymorphisms in the 5' flank of COL1A1 gene and osteoporosis: meta-analysis of published studies
- PMID: 20798928
- PMCID: PMC4696542
- DOI: 10.1007/s00198-010-1364-5
Polymorphisms in the 5' flank of COL1A1 gene and osteoporosis: meta-analysis of published studies
Abstract
A meta-analysis of studies was conducted involving 24,511 participants with 7,864 fractures in which polymorphisms in the 5' flank of COL1A1 (rs1107946, rs2412298, and rs1800012) were related to osteoporosis phenotypes. Polymorphisms of all three sites were associated with BMD, and rs1800012 was associated with fracture but effect sizes were modest.
Introduction and hypothesis: Polymorphisms in the 5' flank of COL1A1 gene have been implicated as genetic markers for susceptibility to osteoporosis, but previous studies have yielded conflicting results.
Methods: We conducted a meta-analysis of 32 studies including 24,511 participants and 7,864 fractures in which alleles at the -1997G/T (rs1107946), -1663in/delT (rs2412298), and Sp1 binding site polymorphisms (rs1800012) of COL1A1 had been related to bone mineral density (BMD) or fracture.
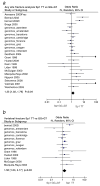
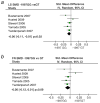
Results: For the Sp1 polymorphism, BMD values in TT homozygotes were 0.13 units [95% CI, 0.03 to 0.24] lower at the spine (p = 0.01) and 0.16 units [0.10 to 0.23] lower at the hip (p = 1 x 10⁻⁶) than GG homozygotes. Clinical fractures were 1.31-fold [1.04-1.65] increased in TT homozygotes (p = 0.02) and vertebral fractures were 1.34-fold [1.01-1.77] increased (p = 0.04). We also observed associations between spine BMD and allelic variants at the -1997G/T (p = 0.05) and the -1663indelT (p = 0.009) sites. We found no association between alleles at the -1997G/T or -1663indelT sites and fracture but power was limited.
Conclusions: The COL1A1 Sp1 polymorphism is associated with a modest reduction in BMD and an increased risk of fracture, although we cannot fully exclude the possibility that the results may have been influenced by publication bias. Further studies are required to fully evaluate the contribution of the -1997G/T and -1663in/delT sites to these phenotypes and to determine if they interact with the Sp1 polymorphism to regulate susceptibility to osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Arden NK, Spector TD. Genetic influences on muscle strength, lean body mass, and bone mineral density: a twin study. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12:2076–2081. - PubMed
-
- Knapp KM, Andrew T, MacGregor AJ, Blake GM, Fogelman I, Spector TD. An investigation of unique and shared gene effects on speed of sound and bone density using axial transmission quantitative ultrasound and DXA in twins. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:1525–1530. - PubMed
-
- Michaelsson K, Melhus H, Ferm H, Ahlbom A, Pedersen NL. Genetic liability to fractures in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:1825–1830. - PubMed
-
- Rivadeneira F, Styrkarsdottir U, Estrada K, Halldorsson BV, Hsu YH, Richards JB, Zillikens MC, Kavvoura FK, Amin N, Aulchenko YS, Cupples LA, Deloukas P, Demissie S, Grundberg E, Hofman A, Kong A, Karasik D, van Meurs JB, Oostra B, Pastinen T, Pols HA, Sigurdsson G, Soranzo N, Thorleifsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Williams FM, Wilson SG, Zhou Y, Ralston SH, van Duijn CM, Spector T, Kiel DP, Stefansson K, Ioannidis JP, Uitterlinden AG. Twenty bone-mineral-density loci identified by large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1119–1206. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Richards JB, Rivadeneira F, Inouye M, Pastinen TM, Soranzo N, Wilson SG, Andrew T, Falchi M, Gwilliam R, Ahmadi KR, Valdes AM, Arp P, Whittaker P, Verlaan DJ, Jhamai M, Kumanduri V, Moorhouse M, van Meurs JB, Hofman A, Pols HA, Hart D, Zhai G, Kato BS, Mullin BH, Zhang F, Deloukas P, Uitterlinden AG, Spector TD. Bone mineral density, osteoporosis, and osteoporotic fractures: a genome-wide association study. Lancet. 2008;371:1505–1512. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

