Structural and magnetic effects of meso-substitution in alkyl-substituted metalloporphyrinate pi-cation radicals: characterization of [Fe(TalkylP*)(Cl)]SbCl6 (alkyl = ethyl and n-propyl)
- PMID: 20799740
- PMCID: PMC2980783
- DOI: 10.1021/ic101099z
Structural and magnetic effects of meso-substitution in alkyl-substituted metalloporphyrinate pi-cation radicals: characterization of [Fe(TalkylP*)(Cl)]SbCl6 (alkyl = ethyl and n-propyl)
Abstract
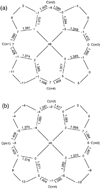
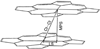
We report the preparation and characterization of two meso-alkyl substituted porphyrin pi-cation radical derivatives, [Fe(TalkylP(*))(Cl)]SbCl(6) (alkyl = ethyl or propyl). Both complexes have been characterized by UV/vis/near-IR, IR, and Mossbauer spectroscopy, temperature-dependent solid-state magnetic susceptibility measurements, and X-ray structure determinations. All data for both oxidized species are consistent with the formulation of the complexes as ring-oxidized iron(III) porphyrin species. The molecular structures of the two five-coordinate species have the typical square-pyramidal coordination group of high-spin iron(III) derivatives. The crystal structures also reveal that the species form cofacial pi-pi dimers with lateral shifts of 1.44 A and 3.22 A, respectively, for the propyl and ethyl radical derivatives. Both radicals exhibit porphyrin cores with alternating bond distance patterns in the inner 16-membered ring. In addition, [Fe(TEtP(*))(Cl)]SbCl(6) and [Fe(TPrP(*))(Cl)]SbCl(6) have been characterized by temperature-dependent (6-300 K) magnetic susceptibility studies, the best fitting of the temperature-dependent moments reveal strong coupling between iron spins and porphyrin radical, and a smaller magnitude of antiferromagnetic coupling between ring radicals, which are opposite to those found in the five-coordinate iron(III) OEP radicals. The differences in structure and properties of the cation radical meso-alkyl and beta-alkyl derivatives possibly reflect differences in properties of a(1u)- and a(2u)-forming radicals.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Metalloporphyrin mixed-valence π-cation radicals: [Fe(oxoOEC(•/2))(Cl)]2SbCl6, structure, magnetic properties, and near-IR spectra.Inorg Chem. 2011 Sep 19;50(18):9114-21. doi: 10.1021/ic201292t. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Inorg Chem. 2011. PMID: 21809820 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic interactions in the high-spin iron(III) oxooctaethylchlorinato derivative [Fe(oxoOEC)(Cl)] and its pi-cation radical [Fe(oxoOEC.)(Cl)]SbCl6.Inorg Chem. 2000 Mar 6;39(5):872-80. doi: 10.1021/ic991052w. Inorg Chem. 2000. PMID: 12526364
-
Factors affecting the electronic ground state of low-spin iron(III) porphyrin complexes.Inorg Chem. 2001 Jul 2;40(14):3423-34. doi: 10.1021/ic001412b. Inorg Chem. 2001. PMID: 11421688
-
Structural deformations and bond length alternation in porphyrin pi-cation radicals.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2001 Sep;6(7):727-32. doi: 10.1007/s007750100274. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2001. PMID: 11681706 Review.
-
Iron corrolates: unambiguous chloroiron(III) (corrolate)(2-.) pi-cation radicals.J Inorg Biochem. 2006 Apr;100(4):810-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2006.01.038. Epub 2006 Mar 7. J Inorg Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16519943 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidation triggers extensive conjugation and unusual stabilization of two di-heme dication diradical intermediates: role of bridging group for electronic communication.Chem Sci. 2016 Feb 1;7(2):1212-1223. doi: 10.1039/c5sc03120f. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 29910877 Free PMC article.
-
Metalloporphyrin mixed-valence π-cation radicals: [Fe(oxoOEC(•/2))(Cl)]2SbCl6, structure, magnetic properties, and near-IR spectra.Inorg Chem. 2011 Sep 19;50(18):9114-21. doi: 10.1021/ic201292t. Epub 2011 Aug 2. Inorg Chem. 2011. PMID: 21809820 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the Ruffled Porphyrin Ring on Electronic Structures: Structure and Characterization of [Fe(TalkylP)(OClO3)] and [Fe(TPrP)(THF)2]ClO4 (alkyl = Ethyl, Et and n-Propyl, Pr).J Porphyr Phthalocyanines. 2013 Jan;17(1n02):118-124. doi: 10.1142/S1088424612501362. J Porphyr Phthalocyanines. 2013. PMID: 23626455 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Abbreviations: TPP, dianion of tetraphenylporphyrin; OEP, dianion of octaethylporphyrin; OEC, dianion of octaethylchlorin; Ca, pyrrole α carbon pyrrole; Cb, β carbon; Cm, methine carbon atom; Np, porphinato nitrogen atom.
-
-
- Song H, Reed CA, Scheidt WR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989;111:6867.
- Song H, Orosz RD, Reed CA, Scheidt WR. Inorg. Chem. 1990;29:4274.
-
- Gans P, Buisson G, Duee E, Marchon J-C, Erler BS, Scholz WF, Reed CA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986;108:1223.
-
- Erler BS, Scholz WF, Lee YJ, Scheidt WR, Reed CA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987;109:2644.
-
- Song H, Reed CA, Scheidt WR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987;111:6865.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

