Role of microRNA-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion
- PMID: 20799954
- PMCID: PMC2939569
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-227
Role of microRNA-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion
Abstract
Background: Micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA)-199a-5p has been reported to be decreased in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) compared to normal tissue. Discoidin domain receptor-1 (DDR1) tyrosine kinase, involved in cell invasion-related signaling pathway, was predicted to be a potential target of miR-199a-5p by the use of miRNA target prediction algorithms. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of miR-199a-5p and DDR1 in HCC invasion.
Methods: Mature miR-199a-5p and DDR1 expression were evaluated in tumor and adjacent non-tumor liver tissues from 23 patients with HCC undergoing liver resection and five hepatoma cell lines by the use of real-time quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis. The effect of aberrant miR-199a-5p expression on cell invasion was assessed in vitro using HepG2 and SNU-182 hepatoma cell lines. Luciferase reporter assay was employed to validate DDR1 as a putative miR-199a-5p target gene. Regulation of DDR1 expression by miR-199a-5p was assessed by the use qRT-PCR and western blotting analysis.
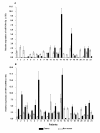
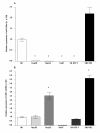
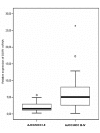
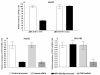
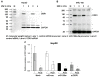
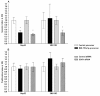
Results: A significant down-regulation of miR-199a-5p was observed in 65.2% of HCC tissues and in four of five cell lines. In contrast, DDR1 expression was significantly increased in 52.2% of HCC samples and in two of five cell lines. Increased DDR1 expression in HCC was associated with advanced tumor stage. DDR1 was shown to be a direct target of miR-199a-5p by luciferase reporter assay. Transfection of miR-199a-5p inhibited invasion of HepG2 but not SNU-182 hepatoma cells.
Conclusions: Decreased expression of miR-199a-5p contributes to increased cell invasion by functional deregulation of DDR1 activity in HCC. However, the effect of miR-199a-5p on DDR1 varies among individuals and hepatoma cell lines. These findings may have significant translational relevance for development of new targeted therapies as well as prognostic prediction for patients with HCC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-199a-5p loss up-regulated DDR1 aggravated colorectal cancer by activating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition related signaling.Dig Dis Sci. 2014 Sep;59(9):2163-72. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3136-0. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Dig Dis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24711074
-
MiR-199a-5p suppresses tumorigenesis by targeting clathrin heavy chain in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Biochem Funct. 2017 Mar;35(2):98-104. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3252. Epub 2017 Mar 5. Cell Biochem Funct. 2017. PMID: 28261837
-
MiR-199a-5p and let-7c cooperatively inhibit migration and invasion by targeting MAP4K3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13666-13677. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14623. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28099144 Free PMC article.
-
Discoidin Domain Receptor 1, a Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Feb 23;15:2037-2044. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S348110. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35237068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research Progress of Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 in Breast Cancer and Other Malignant Tumors].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2021 Aug;43(4):634-641. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.13315. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34494537 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
MiR-138 induces cell cycle arrest by targeting cyclin D3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Carcinogenesis. 2012 May;33(5):1113-20. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs113. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22362728 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miRNA-122, miRNA-199a, and miRNA-16 as Biomarkers for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Mol Diagn Ther. 2015 Aug;19(4):213-20. doi: 10.1007/s40291-015-0148-1. Mol Diagn Ther. 2015. PMID: 26133725
-
Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 Expression in Colon Cancer: Roles and Prognosis Impact.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 13;14(4):928. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040928. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205677 Free PMC article.
-
A novel functional crosstalk between DDR1 and the IGF axis and its relevance for breast cancer.Cell Adh Migr. 2018;12(4):305-314. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2018.1445953. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 29486622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression analysis of liver-specific circulating microRNAs in HCV-induced hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian patients.Cancer Biol Ther. 2018 May 4;19(5):400-406. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1423922. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29333940 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

