Folding, DNA recognition, and function of GIY-YIG endonucleases: crystal structures of R.Eco29kI
- PMID: 20800503
- PMCID: PMC2955809
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2010.07.006
Folding, DNA recognition, and function of GIY-YIG endonucleases: crystal structures of R.Eco29kI
Abstract
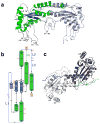
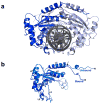
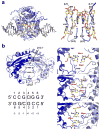
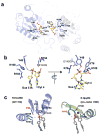
The GIY-YIG endonuclease family comprises hundreds of diverse proteins and a multitude of functions; none have been visualized bound to DNA. The structure of the GIY-YIG restriction endonuclease R.Eco29kI has been solved both alone and bound to its target site. The protein displays a domain-swapped homodimeric structure with several extended surface loops encircling the DNA. Only three side chains from each protein subunit contact DNA bases, two directly and one via a bridging solvent molecule. Both tyrosine residues within the GIY-YIG motif are positioned in the catalytic center near a putative nucleophilic water; the remainder of the active site resembles the HNH endonuclease family. The structure illustrates how the GIY-YIG scaffold has been adapted for the highly specific recognition of a DNA restriction site, in contrast to nonspecific DNA cleavage by GIY-YIG domains in homing endonucleases or structure-specific cleavage by DNA repair enzymes such as UvrC.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Type II restriction endonuclease R.Eco29kI is a member of the GIY-YIG nuclease superfamily.BMC Struct Biol. 2007 Jul 12;7:48. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-7-48. BMC Struct Biol. 2007. PMID: 17626614 Free PMC article.
-
Type II restriction endonuclease R.Hpy188I belongs to the GIY-YIG nuclease superfamily, but exhibits an unusual active site.BMC Struct Biol. 2008 Nov 14;8:48. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-8-48. BMC Struct Biol. 2008. PMID: 19014591 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomeric structure diversity within the GIY-YIG nuclease family.J Mol Biol. 2009 Mar 20;387(1):10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.048. Epub 2009 Jan 30. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19361436
-
Catalytic mechanisms of restriction and homing endonucleases.Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 26;41(47):13851-60. doi: 10.1021/bi020467h. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12437341 Review.
-
Type II restriction endonucleases: structure and mechanism.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Mar;62(6):685-707. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4513-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15770420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of a Novel N4-Methylcytosine Restriction-Modification System in Deinococcus radiodurans.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 29;25(3):1660. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031660. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338939 Free PMC article.
-
GEN1 from a thermophilic fungus is functionally closely similar to non-eukaryotic junction-resolving enzymes.J Mol Biol. 2014 Dec 12;426(24):3946-3959. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.10.008. Epub 2014 Oct 12. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25315822 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphic toxin systems: Comprehensive characterization of trafficking modes, processing, mechanisms of action, immunity and ecology using comparative genomics.Biol Direct. 2012 Jun 25;7:18. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-7-18. Biol Direct. 2012. PMID: 22731697 Free PMC article.
-
Gene flow and biological conflict systems in the origin and evolution of eukaryotes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Jun 29;2:89. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00089. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22919680 Free PMC article.
-
Holliday junction resolution by At-HIGLE: an SLX1 lineage endonuclease from Arabidopsis thaliana with a novel in-built regulatory mechanism.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 May 6;50(8):4630-4646. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac239. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35412622 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

