Helicobacter pylori infection promotes methylation and silencing of trefoil factor 2, leading to gastric tumor development in mice and humans
- PMID: 20801119
- PMCID: PMC3970568
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.08.043
Helicobacter pylori infection promotes methylation and silencing of trefoil factor 2, leading to gastric tumor development in mice and humans
Abstract
Background & aims: Trefoil factors (TFFs) regulate mucosal repair and suppress tumor formation in the stomach. Tff1 deficiency results in gastric cancer, whereas Tff2 deficiency increases gastric inflammation. TFF2 expression is frequently lost in gastric neoplasms, but the nature of the silencing mechanism and associated impact on tumorigenesis have not been determined.
Methods: We investigated the epigenetic silencing of TFF2 in gastric biopsy specimens from individuals with Helicobacter pylori-positive gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, gastric cancer, and disease-free controls. TFF2 function and methylation were manipulated in gastric cancer cell lines. The effects of Tff2 deficiency on tumor growth were investigated in the gp130(F/F) mouse model of gastric cancer.
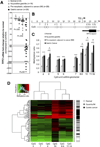
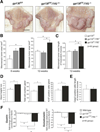
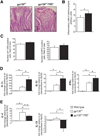
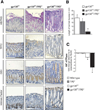
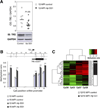
Results: In human tissue samples, DNA methylation at the TFF2 promoter began at the time of H pylori infection and increased throughout gastric tumor progression. TFF2 methylation levels were inversely correlated with TFF2 messenger RNA levels and could be used to discriminate between disease-free controls, H pylori-infected, and tumor tissues. Genome demethylation restored TFF2 expression in gastric cancer cell lines, so TFF2 silencing requires methylation. In Tff2-deficient gp130(F/F)/Tff2(-/-) mice, proliferation of mucosal cells and release of T helper cell type-1 (Th-1) 1 cytokines increased, whereas expression of gastric tumor suppressor genes and Th-2 cytokines were reduced, compared with gp130(F/F)controls. The fundus of gp130(F/F)/Tff2(-/-) mice displayed glandular atrophy and metaplasia, indicating accelerated preneoplasia. Experimental H pylori infection in wild-type mice reduced antral expression of Tff2 by increased promoter methylation.
Conclusions: TFF2 negatively regulates preneoplastic progression and subsequent tumor development in the stomach, a role that is subverted by promoter methylation during H pylori infection.
Copyright © 2010 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures

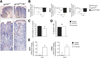
References
-
- Wright NA, Hoffmann W, Otto WR, et al. Rolling in the clover: trefoil factor family (TFF)-domain peptides, cell migration and cancer. FEBS Lett. 1997;408:121–123. - PubMed
-
- Taupin DR, Pang KC, Green SP, et al. The trefoil peptides spasmolytic polypeptide and intestinal trefoil factor are major secretory products of the rat gut. Peptides. 1995;16:1001–1005. - PubMed
-
- Kindon H, Pothoulakis C, Thim L, et al. Trefoil peptide protection of intestinal epithelial barrier function: cooperative interaction with mucin glycoprotein. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:516–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

