Use of virtual cell in studies of cellular dynamics
- PMID: 20801417
- PMCID: PMC3519358
- DOI: 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)83001-1
Use of virtual cell in studies of cellular dynamics
Abstract
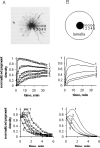
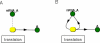
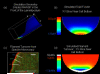
The Virtual Cell (VCell) is a unique computational environment for modeling and simulation of cell biology. It has been specifically designed to be a tool for a wide range of scientists, from experimental cell biologists to theoretical biophysicists. The models created with VCell can range from the simple, to evaluate hypotheses or to interpret experimental data, to complex multilayered models used to probe the predicted behavior of spatially resolved, highly nonlinear systems. In this chapter, we discuss modeling capabilities of VCell and demonstrate representative examples of the models published by the VCell users.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
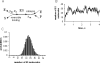
Similar articles
-
Quantitative cell biology with the Virtual Cell.Trends Cell Biol. 2003 Nov;13(11):570-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2003.09.002. Trends Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14573350 Review.
-
Virtual Cell: computational tools for modeling in cell biology.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2012 Mar-Apr;4(2):129-40. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.165. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22139996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rule-based modeling with Virtual Cell.Bioinformatics. 2016 Sep 15;32(18):2880-2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw353. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27497444 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Cell modelling and simulation software environment.IET Syst Biol. 2008 Sep;2(5):352-62. doi: 10.1049/iet-syb:20080102. IET Syst Biol. 2008. PMID: 19045830 Free PMC article.
-
Compartmental and Spatial Rule-Based Modeling with Virtual Cell.Biophys J. 2017 Oct 3;113(7):1365-1372. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.08.022. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28978431 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Developing models in virtual cell.Sci Signal. 2011 Sep 20;4(192):tr12. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2001970. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 21954293 Free PMC article.
-
Ten steps to investigate a cellular system with mathematical modeling.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 May 13;17(5):e1008921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008921. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33983922 Free PMC article.
-
Redundant mechanisms for stable cell locomotion revealed by minimal models.Biophys J. 2011 Aug 3;101(3):545-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.06.032. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21806922 Free PMC article.
-
Recycling of kinesin-1 motors by diffusion after transport.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 30;8(9):e76081. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076081. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098765 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the influence of cytosolic and membrane FAK activation on YAP/TAZ nuclear translocation.Biophys J. 2021 Oct 19;120(20):4360-4377. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.09.009. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 34509508 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

