Genetic variants in ABCB1 and CYP2C19 and cardiovascular outcomes after treatment with clopidogrel and prasugrel in the TRITON-TIMI 38 trial: a pharmacogenetic analysis
- PMID: 20801494
- PMCID: PMC3036672
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61273-1
Genetic variants in ABCB1 and CYP2C19 and cardiovascular outcomes after treatment with clopidogrel and prasugrel in the TRITON-TIMI 38 trial: a pharmacogenetic analysis
Abstract
Background: Clopidogrel and prasugrel are subject to efflux via P-glycoprotein (encoded by ABCB1, also known as MDR1). ABCB1 polymorphisms, particularly 3435C→T, may affect drug transport and efficacy. We aimed to assess the effect of this polymorphism by itself and alongside variants in CYP2C19 on cardiovascular outcomes in patients treated with clopidogrel or prasugrel in TRITON-TIMI 38. We also assessed the effect of genotype on the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of these drugs in healthy individuals.
Methods: We genotyped ABCB1 in 2932 patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous intervention who were treated with clopidogrel (n=1471) or prasugrel (n=1461) in the TRITON-TIMI 38 trial. We evaluated the association between ABCB1 3435C→T and rates of the primary efficacy endpoint (cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke) until 15 months. We then assessed the combined effect of ABCB1 3435C→T genotype and reduced-function alleles of CYP2C19. 321 healthy individuals were also genotyped, and we tested the association of genetic variants with reduction in maximum platelet aggregation and plasma concentrations of active drug metabolites.
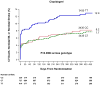
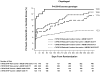
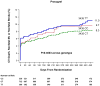
Findings: In patients treated with clopidogrel, ABCB1 3435C→T genotype was significantly associated with the risk of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke (p=0·0064). TT homozygotes had a 72% increased risk of the primary endpoint compared with CT/CC individuals (Kaplan-Meier event rates 12·9% [52 of 414] vs 7·8% [80 of 1057 participants]; HR 1·72, 95% CI 1·22-2·44, p=0·002). ABCB1 3435C→T and CYP2C19 genotypes were significant, independent predictors of the primary endpoint, and 681 (47%) of the 1454 genotyped patients taking clopidogrel who were either CYP2C19 reduced-function allele carriers, ABCB1 3435 TT homozygotes, or both were at increased risk of the primary endpoint (HR 1·97, 95% CI 1·38-2·82, p=0·0002). In healthy participants, 3435 TT homozygotes had an absolute reduction in maximum platelet aggregation with clopidogrel that was 7·3 percentage points less than for CT/CC individuals (p=0·0127). ABCB1 genotypes were not significantly associated with clinical or pharmacological outcomes in patients with an acute coronary syndrome or healthy individuals treated with prasugrel, respectively.
Interpretation: Individuals with the ABCB1 3435 TT genotype have reduced platelet inhibition and are at increased risk of recurrent ischaemic events during clopidogrel treatment. In patients with acute coronary syndromes who have undergone percutaneous intervention, when both ABCB1 and CYP2C19 are taken into account, nearly half of the population carries a genotype associated with increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events while on standard doses of clopidogrel.
Funding: Daiichi Sankyo Company Ltd and Eli Lilly and Company.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Response to antiplatelet treatment: from genes to outcome.Lancet. 2010 Oct 16;376(9749):1278-81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61313-X. Lancet. 2010. PMID: 20801497 No abstract available.
-
Pharmacogenetics: Clinical response to antiplatelet therapy--how much does genotype count?Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010 Nov;7(11):597. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.146. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 21080597 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, Bridges CR, Califf RM, Casey DE, Jr, Chavey WE, 2nd, Fesmire FM, Hochman JS, Levin TN, Lincoff AM, Peterson ED, Theroux P, Wenger NK, Wright RS, Smith SC, Jr, Jacobs AK, Halperin JL, Hunt SA, Krumholz HM, Kushner FG, Lytle BW, Nishimura R, Ornato JP, Page RL, Riegel B. ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-Elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) developed in collaboration with the American College of Emergency Physicians, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons endorsed by the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation and the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50(7):e1–e157. - PubMed
-
- Kushner FG, Hand M, Smith SC, Jr, King SB, 3rd, Anderson JL, Antman EM, Bailey SR, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, Casey DE, Jr, Green LA, Hochman JS, Jacobs AK, Krumholz HM, Morrison DA, Ornato JP, Pearle DL, Peterson ED, Sloan MA, Whitlow PL, Williams DO. 2009 Focused Updates: ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Management of Patients With ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (updating the 2004 Guideline and 2007 Focused Update) and ACC/AHA/SCAI Guidelines on Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (updating the 2005 Guideline and 2007 Focused Update): a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2009;120(22):2271–2306. - PubMed
-
- Gurbel PA, Bliden KP, Hiatt BL, O'Connor CM. Clopidogrel for coronary stenting: response variability, drug resistance, and the effect of pretreatment platelet reactivity. Circulation. 2003;107(23):2908–2913. - PubMed
-
- Hochholzer W, Trenk D, Bestehorn HP, Fischer B, Valina CM, Ferenc M, Gick M, Caputo A, Buttner HJ, Neumann FJ. Impact of the degree of peri-interventional platelet inhibition after loading with clopidogrel on early clinical outcome of elective coronary stent placement. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(9):1742–1750. - PubMed
-
- Wiviott SD, Trenk D, Frelinger AL, O'Donoghue M, Neumann FJ, Michelson AD, Angiolillo DJ, Hod H, Montalescot G, Miller DL, Jakubowski JA, Cairns R, Murphy SA, McCabe CH, Antman EM, Braunwald E. Prasugrel compared with high loading- and maintenance-dose clopidogrel in patients with planned percutaneous coronary intervention: the Prasugrel in Comparison to Clopidogrel for Inhibition of Platelet Activation and Aggregation-Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 44 trial. Circulation. 2007;116(25):2923–2932. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

