Chromosome 9p21 in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the UK and seven other countries: a genome-wide association study
- PMID: 20801717
- PMCID: PMC3257853
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70197-6
Chromosome 9p21 in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the UK and seven other countries: a genome-wide association study
Erratum in
- Lancet Neurol. 2011 Mar;10(3):205
Abstract
Background: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease of motor neurons that results in progressive weakness and death from respiratory failure, commonly within about 3 years. Previous studies have shown association of a locus on chromosome 9p with ALS and linkage with ALS-frontotemporal dementia. We aimed to test whether this genomic region is also associated with ALS in an independent set of UK samples, and to identify risk factors associated with ALS in a further genome-wide association study that combined data from the independent analysis with those from other countries.
Methods: We collected samples from patients with sporadic ALS from 20 UK hospitals and obtained UK control samples from the control groups of the Depression Case Control study, the Bipolar Affective Case Control Study, and the British 1958 birth cohort DNA collection. Genotyping of DNA in this independent analysis was done with Illumina HumanHap550 BeadChips. We then undertook a joint genome-wide analysis that combined data from the independent set with published data from the UK, USA, Netherlands, Ireland, Italy, France, Sweden, and Belgium. The threshold for significance was p=0·05 in the independent analysis, because we were interested in replicating a small number of previously reported associations, whereas the Bonferroni-corrected threshold for significance in the joint analysis was p=2·20×10(-7)
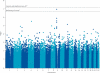
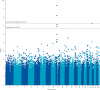
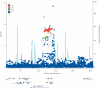
Findings: After quality control, samples were available from 599 patients and 4144 control individuals in the independent set. In this analysis, two single nucleotide polymorphisms in a locus on chromosome 9p21.2 were associated with ALS: rs3849942 (p=2·22×10(-6); odds ratio [OR] 1·39, 95% CI 1·21-1·59) and rs2814707 (p=3·32×10(-6); 1·38, 1·20-1·58). In the joint analysis, which included samples from 4312 patients with ALS and 8425 control individuals, rs3849942 (p=4·64×10(-10); OR 1·22, 95% CI 1·15-1·30) and rs2814707 (p=4·72×10(-10); 1·22, 1·15-1·30) were associated with ALS.
Interpretation: We have found strong evidence of a genetic association of two single nucleotide polymorphisms on chromosome 9 with sporadic ALS, in line with findings from previous independent GWAS of ALS and linkage studies of ALS-frontotemporal dementia. Our findings together with these earlier findings suggest that genetic variation at this locus on chromosome 9 causes sporadic ALS and familial ALS-frontotemporal dementia. Resequencing studies and then functional analysis should be done to identify the defective gene.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Chromosome 9p21 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: the plot thickens.Lancet Neurol. 2010 Oct;9(10):945-7. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70211-8. Lancet Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20801719 No abstract available.
References
-
- Johnston CA, Stanton BR, Turner MR. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in an urban setting: a population based study of inner city London. J Neurol. 2006;253:1642–1643. - PubMed
-
- Morita M, Al-Chalabi A, Andersen PM. A locus on chromosome 9p confers susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Neurology. 2006;66:839–844. - PubMed
-
- Vance C, Al-Chalabi A, Ruddy D. Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with frontotemporal dementia is linked to a locus on chromosome 9p13.2-21.3. Brain. 2006;129:868–876. - PubMed
-
- Valdmanis PN, Dupre N, Bouchard JP. Three families with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia with evidence of linkage to chromosome 9p. Arch Neurol. 2007;64:240–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 089701/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- Z01 AG000949/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600974/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 070122/A/02/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0701420/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601943/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0900688/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01-AG000949-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

