A novel six-rhodopsin system in a single archaeon
- PMID: 20802037
- PMCID: PMC2976437
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00642-10
A novel six-rhodopsin system in a single archaeon
Abstract
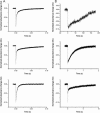
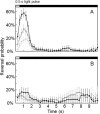
Microbial rhodopsins, a diverse group of photoactive proteins found in Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya, function in photosensing and photoenergy harvesting and may have been present in the resource-limited early global environment. Four different physiological functions have been identified and characterized for nearly 5,000 retinal-binding photoreceptors, these being ion transporters that transport proton or chloride and sensory rhodopsins that mediate light-attractant and/or -repellent responses. The greatest number of rhodopsins previously observed in a single archaeon had been four. Here, we report a newly discovered six-rhodopsin system in a single archaeon, Haloarcula marismortui, which shows a more diverse absorbance spectral distribution than any previously known rhodopsin system, and, for the first time, two light-driven proton transporters that respond to the same wavelength. All six rhodopsins, the greatest number ever identified in a single archaeon, were first shown to be expressed in H. marismortui, and these were then overexpressed in Escherichia coli. The proteins were purified for absorption spectra and photocycle determination, followed by measurement of ion transportation and phototaxis. The results clearly indicate the existence of a proton transporter system with two isochromatic rhodopsins and a new type of sensory rhodopsin-like transducer in H. marismortui.
Figures




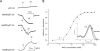

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of Different Types of Microbial Rhodopsins with a Highly Expressible Bacteriorhodopsin from Haloarcula marismortui as a Single Protein in E. coli.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 19;8(1):14026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32399-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30232361 Free PMC article.
-
The Blue-Green Sensory Rhodopsin SRM from Haloarcula marismortui Attenuates Both Phototactic Responses Mediated by Sensory Rhodopsin I and II in Halobacterium salinarum.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 5;9(1):5672. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42193-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30952934 Free PMC article.
-
A microbial rhodopsin with a unique retinal composition shows both sensory rhodopsin II and bacteriorhodopsin-like properties.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):5967-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.190058. Epub 2010 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21135094 Free PMC article.
-
History and Perspectives of Ion-Transporting Rhodopsins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1293:3-19. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-8763-4_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33398804 Review.
-
Light-driven ion-translocating rhodopsins in marine bacteria.Trends Microbiol. 2015 Feb;23(2):91-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.10.009. Trends Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25432080 Review.
Cited by
-
Marine Bacterial and Archaeal Ion-Pumping Rhodopsins: Genetic Diversity, Physiology, and Ecology.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Sep 14;80(4):929-54. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00003-16. Print 2016 Dec. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27630250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HwMR is a novel magnesium-associated protein.Biophys J. 2022 Jul 19;121(14):2781-2793. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.06.010. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35690905 Free PMC article.
-
Complete Genome Sequence of a New Halophilic Archaeon, Haloarcula taiwanensis, Isolated from a Solar Saltern in Southern Taiwan.Genome Announc. 2018 Feb 1;6(5):e01529-17. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01529-17. Genome Announc. 2018. PMID: 29437098 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved Trp residue in HwBR contributes to its unique tolerance toward acidic environments.Biophys J. 2022 Aug 16;121(16):3136-3145. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.07.009. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35808832 Free PMC article.
-
The photochemical determinants of color vision: revealing how opsins tune their chromophore's absorption wavelength.Bioessays. 2014 Jan;36(1):65-74. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300094. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Bioessays. 2014. PMID: 24323922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Baliga, N. S., R. Bonneau, M. T. Facciotti, M. Pan, G. Glusman, E. W. Deutsch, P. Shannon, Y. Chiu, R. S. Weng, R. R. Gan, P. Hung, S. V. Date, E. Marcotte, L. Hood, and W. V. Ng. 2004. Genome sequence of Haloarcula marismortui: a halophilic archaeon from the Dead Sea. Genome Res. 14:2221-2234. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

