Mechanism of positive regulation by DsrA and RprA small noncoding RNAs: pairing increases translation and protects rpoS mRNA from degradation
- PMID: 20802038
- PMCID: PMC2953674
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00464-10
Mechanism of positive regulation by DsrA and RprA small noncoding RNAs: pairing increases translation and protects rpoS mRNA from degradation
Abstract
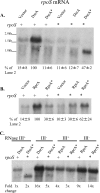
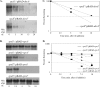
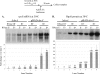
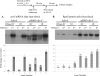
Small noncoding RNAs (sRNAs) regulate gene expression in Escherichia coli by base pairing with mRNAs and modulating translation and mRNA stability. The sRNAs DsrA and RprA stimulate the translation of the stress response transcription factor RpoS by base pairing with the 5' untranslated region of the rpoS mRNA. In the present study, we found that the rpoS mRNA was unstable in the absence of DsrA and RprA and that expression of these sRNAs increased both the accumulation and the half-life of the rpoS mRNA. Mutations in dsrA, rprA, or rpoS that disrupt the predicted pairing sequences and reduce translation of RpoS also destabilize the rpoS mRNA. We found that the rpoS mRNA accumulates in an RNase E mutant strain in the absence of sRNA expression and, therefore, is degraded by an RNase E-mediated mechanism. DsrA expression is required, however, for maximal translation even when rpoS mRNA is abundant. This suggests that DsrA protects rpoS mRNA from degradation by RNase E and that DsrA has a further activity in stimulating RpoS protein synthesis. rpoS mRNA is subject to degradation by an additional pathway, mediated by RNase III, which, in contrast to the RNase E-mediated pathway, occurs in the presence and absence of DsrA or RprA. rpoS mRNA and RpoS protein levels are increased in an RNase III mutant strain with or without the sRNAs, suggesting that the role of RNase III in this context is to reduce the translation of RpoS even when the sRNAs are acting to stimulate translation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of Hfq on RprA-rpoS mRNA pairing: Hfq-RNA binding and the influence of the 5' rpoS mRNA leader region.Biochemistry. 2008 Oct 28;47(43):11184-95. doi: 10.1021/bi800479p. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18826256
-
Regulation of RpoS by a novel small RNA: the characterization of RprA.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Mar;39(5):1382-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2001.02329.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11251852
-
Turn-over of the small non-coding RNA RprA in E. coli is influenced by osmolarity.Mol Genet Genomics. 2010 Oct;284(4):307-18. doi: 10.1007/s00438-010-0568-x. Epub 2010 Aug 18. Mol Genet Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20717695
-
Small non-coding RNAs, co-ordinators of adaptation processes in Escherichia coli: the RpoS paradigm.Mol Microbiol. 2003 May;48(4):855-61. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03454.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12753181 Review.
-
The small RNA regulators of Escherichia coli: roles and mechanisms*.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2004;58:303-28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.58.030603.123841. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15487940 Review.
Cited by
-
Antagonistic functions between the RNA chaperone Hfq and an sRNA regulate sensitivity to the antibiotic colicin.EMBO J. 2013 Oct 16;32(20):2764-78. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.205. Epub 2013 Sep 24. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 24065131 Free PMC article.
-
Domain swapping between homologous bacterial small RNAs dissects processing and Hfq binding determinants and uncovers an aptamer for conditional RNase E cleavage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 29;44(2):824-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1161. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26531825 Free PMC article.
-
Role of polynucleotide phosphorylase in sRNA function in Escherichia coli.RNA. 2011 Jun;17(6):1172-89. doi: 10.1261/rna.2531211. Epub 2011 Apr 28. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21527671 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for Involvement of the Salmonella enterica Z-Ring Assembly Factors ZapA and ZapB in Resistance to Bile.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 25;12:647305. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.647305. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33717045 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in fish-pathogenic bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2015 Jul 9;6:700. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00700. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26217329 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Argaman, L., R. Hershberg, J. Vogel, G. Bejerano, E. G. H. Wagner, H. Margalit, and S. Altuvia. 2001. Novel small RNA-encoding genes in the intergenic region of Escherichia coli. Curr. Biol. 11:941-950. - PubMed
-
- Basineni, S. R., R. Madhugiri, T. Kolmsee, R. Hengge, and G. Klug. 2009. The influence of Hfq and ribonucleases on the stability of the small non-coding RNA OxyS and its target rpoS in E. coli is growth phase dependent. RNA Biol. 6:584-594. - PubMed
-
- Bougdour, A., C. Cunning, P. J. Baptiste, T. Elliott, and S. Gottesman. 2008. Multiple pathways for regulation of σS (RpoS) stability in Escherichia coli via the action of multiple anti-adaptors. Mol. Microbiol. 68:298-313. - PubMed
-
- Brennan, R. G., and T. M. Link. 2007. Hfq structure, function and ligand binding. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10:125-133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

