The elemental sulfur-responsive protein (SipA) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus is regulated by sulfide in an iron-dependent manner
- PMID: 20802041
- PMCID: PMC2953673
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00660-10
The elemental sulfur-responsive protein (SipA) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus is regulated by sulfide in an iron-dependent manner
Abstract
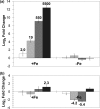
The gene (sipA) encoding the sulfur-induced protein A (PF2025) is highly upregulated during growth of Pyrococcus furiosus on elemental sulfur (S(0)). Expression of sipA is regulated by sulfide, the product of S(0) reduction, but in an iron-dependent manner. SipA is proposed to play a role in intracellular iron sulfide detoxification.
Figures

References
-
- Adams, M. W. W., J. F. Holden, A. L. Menon, G. J. Schut, A. M. Grunden, C. Hou, A. M. Hutchins, F. E. Jenney, Jr., C. Kim, K. Ma, G. Pan, R. Roy, R. Sapra, S. V. Story, and M. F. J. M. Verhagen. 2001. Key role for sulfur in peptide metabolism and in regulation of three hydrogenases in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J. Bacteriol. 183:716-724. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amend, J. P., and E. L. Shock. 2001. Energetics of overall metabolic reactions of thermophilic and hyperthermophilic archaea and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 25:175-243. - PubMed
-
- Birkett, C. R., K. E. Foster, L. Johnson, and K. Gull. 1985. Use of monoclonal antibodies to analyse the expression of a multi-tubulin family. FEBS Lett. 187:211-218. - PubMed
-
- Fiala, G., and K. O. Stetter. 1986. Pyrococcus furiosus sp. nov. represents a novel genus of marine heterotrophic archaebacteria growing optimally at 100° C. Arch. Microbiol. 145:56-61.
-
- Hatton, B., and D. Rickard. 2008. Nucleic acids bind to nanoparticulate iron (II) monosulphide in aqueous solutions. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 38:257-270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

