Construction of a large extracellular protein interaction network and its resolution by spatiotemporal expression profiling
- PMID: 20802085
- PMCID: PMC3101854
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M110.004119
Construction of a large extracellular protein interaction network and its resolution by spatiotemporal expression profiling
Abstract
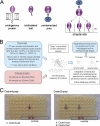
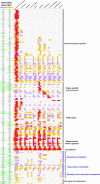
Extracellular interactions involving both secreted and membrane-tethered receptor proteins are essential to initiate signaling pathways that orchestrate cellular behaviors within biological systems. Because of the biochemical properties of these proteins and their interactions, identifying novel extracellular interactions remains experimentally challenging. To address this, we have recently developed an assay, AVEXIS (avidity-based extracellular interaction screen) to detect low affinity extracellular interactions on a large scale and have begun to construct interaction networks between zebrafish receptors belonging to the immunoglobulin and leucine-rich repeat protein families to identify novel signaling pathways important for early development. Here, we expanded our zebrafish protein library to include other domain families and many more secreted proteins and performed our largest screen to date totaling 16,544 potential unique interactions. We report 111 interactions of which 96 are novel and include the first documented extracellular ligands for 15 proteins. By including 77 interactions from previous screens, we assembled an expanded network of 188 extracellular interactions between 92 proteins and used it to show that secreted proteins have twice as many interaction partners as membrane-tethered receptors and that the connectivity of the extracellular network behaves as a power law. To try to understand the functional role of these interactions, we determined new expression patterns for 164 genes within our clone library by using whole embryo in situ hybridization at five key stages of zebrafish embryonic development. These expression data were integrated with the binding network to reveal where each interaction was likely to function within the embryo and were used to resolve the static interaction network into dynamic tissue- and stage-specific subnetworks within the developing zebrafish embryo. All these data were organized into a freely accessible on-line database called ARNIE (AVEXIS Receptor Network with Integrated Expression; www.sanger.ac.uk/arnie) and provide a valuable resource of new extracellular signaling interactions for developmental biology.
Figures



References
-
- van der Merwe P. A., Barclay A. N. (1994) Transient intercellular adhesion: the importance of weak protein-protein interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 19, 354–358 - PubMed
-
- Urech D. M., Lichtlen P., Barberis A. (2003) Cell growth selection system to detect extracellular and transmembrane protein interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1622, 117–127 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

