Physical temperature effects on trust behavior: the role of insula
- PMID: 20802090
- PMCID: PMC3150863
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsq077
Physical temperature effects on trust behavior: the role of insula
Abstract
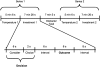
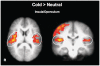
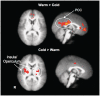
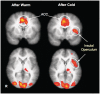
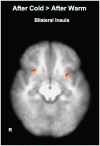
Trust lies at the heart of person perception and interpersonal decision making. In two studies, we investigated physical temperature as one factor that can influence human trust behavior, and the insula as a possible neural substrate. Participants briefly touched either a cold or warm pack, and then played an economic trust game. Those primed with cold invested less with an anonymous partner, revealing lesser interpersonal trust, as compared to those who touched a warm pack. In Study 2, we examined neural activity during trust-related processes after a temperature manipulation using functional magnetic resonance imaging. The left-anterior insular region activated more strongly than baseline only when the trust decision was preceded by touching a cold pack, and not a warm pack. In addition, greater activation within bilateral insula was identified during the decision phase followed by a cold manipulation, contrasted to warm. These results suggest that the insula may be a key shared neural substrate that mediates the influence of temperature on trust processes.
Figures
References
-
- Barsalou LW. Perceptual symbol systems. Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 1999;22:577–660. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A. Disturbances of emotion regulation after focal brain lesions. International Review Of Neurobiology. 2004;62:159–93. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A. Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Natural Neuroscience. 2005;8:1458–63. - PubMed
-
- Berg J, Dickhaut J, McCabe K. Trust, reciprocity, and social history. Games and Economic Behavior. 1995;10:122–42.

