CGI-58 knockdown in mice causes hepatic steatosis but prevents diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance
- PMID: 20802159
- PMCID: PMC2952571
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M010256
CGI-58 knockdown in mice causes hepatic steatosis but prevents diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance
Abstract
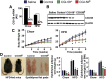
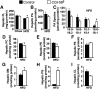
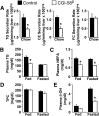
Mutations of Comparative Gene Identification-58 (CGI-58) in humans cause triglyceride (TG) accumulation in multiple tissues. Mice genetically lacking CGI-58 die shortly after birth due to a skin barrier defect. To study the role of CGI-58 in integrated lipid and energy metabolism, we utilized antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) to inhibit CGI-58 expression in adult mice. Treatment with two distinct CGI-58-targeting ASOs resulted in ∼80-95% knockdown of CGI-58 protein expression in both liver and white adipose tissue. In chow-fed mice, ASO-mediated depletion of CGI-58 did not alter weight gain, plasma TG, or plasma glucose, yet raised hepatic TG levels ∼4-fold. When challenged with a high-fat diet (HFD), CGI-58 ASO-treated mice were protected against diet-induced obesity, but their hepatic contents of TG, diacylglycerols, and ceramides were all elevated, and intriguingly, their hepatic phosphatidylglycerol content was increased by 10-fold. These hepatic lipid alterations were associated with significant decreases in hepatic TG hydrolase activity, hepatic lipoprotein-TG secretion, and plasma concentrations of ketones, nonesterified fatty acids, and insulin. Additionally, HFD-fed CGI-58 ASO-treated mice were more glucose tolerant and insulin sensitive. Collectively, this work demonstrates that CGI-58 plays a critical role in limiting hepatic steatosis and maintaining hepatic glycerophospholipid homeostasis and has unmasked an unexpected role for CGI-58 in promoting HFD-induced obesity and insulin resistance.
Figures


References
-
- Igal R. A., Rhoads J. M., Coleman R. A. 1997. Neutral lipid storage disease with fatty liver and cholestasis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 25: 541–547. - PubMed
-
- Dorfman M. L., Hershko C., Eisenberg S., Sagher F. 1974. Ichthyosiform dermatosis with systemic lipidosis. Arch. Dermatol. 110: 261–266. - PubMed
-
- Lefevre C., Jobard F., Caux F., Bouadjar B., Karaduman A., Heilig R., Lakhdar H., Wollenberg A., Verret J. L., Weissenbach J., et al. 2001. Mutations in CGI-58, the gene encoding a new protein of the esterase/lipase/thioesterase subfamily, in Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69: 1002–1012. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hilaire N., Negre-Salvayre A., Salvayre R. 1993. Cytoplasmic triacylglycerols and cholesteryl esters are degraded in two separate catabolic pools in cultured human fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 328: 230–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1K99-HL096166-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01HL057278-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01HL049373-17/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL049373/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL096166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK084582/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL096166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32DK084582-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL091797/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK085176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

