Conditional gene targeting in mouse pancreatic ß-Cells: analysis of ectopic Cre transgene expression in the brain
- PMID: 20802254
- PMCID: PMC2992770
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0624
Conditional gene targeting in mouse pancreatic ß-Cells: analysis of ectopic Cre transgene expression in the brain
Abstract
Objective: Conditional gene targeting has been extensively used for in vivo analysis of gene function in β-cell biology. The objective of this study was to examine whether mouse transgenic Cre lines, used to mediate β-cell- or pancreas-specific recombination, also drive Cre expression in the brain.
Research design and methods: Transgenic Cre lines driven by Ins1, Ins2, and Pdx1 promoters were bred to R26R reporter strains. Cre activity was assessed by β-galactosidase or yellow fluorescent protein expression in the pancreas and the brain. Endogenous Pdx1 gene expression was monitored using Pdx1(tm1Cvw) lacZ knock-in mice. Cre expression in β-cells and co-localization of Cre activity with orexin-expressing and leptin-responsive neurons within the brain was assessed by immunohistochemistry.
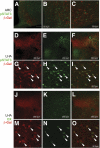
Results: All transgenic Cre lines examined that used the Ins2 promoter to drive Cre expression showed widespread Cre activity in the brain, whereas Cre lines that used Pdx1 promoter fragments showed more restricted Cre activity primarily within the hypothalamus. Immunohistochemical analysis of the hypothalamus from Tg(Pdx1-cre)(89.1Dam) mice revealed Cre activity in neurons expressing orexin and in neurons activated by leptin. Tg(Ins1-Cre/ERT)(1Lphi) mice were the only line that lacked Cre activity in the brain.
Conclusions: Cre-mediated gene manipulation using transgenic lines that express Cre under the control of the Ins2 and Pdx1 promoters are likely to alter gene expression in nutrient-sensing neurons. Therefore, data arising from the use of these transgenic Cre lines must be interpreted carefully to assess whether the resultant phenotype is solely attributable to alterations in the islet β-cells.
Figures


Comment in
-
The hypothalamus and ß-cell connection in the gene-targeting era.Diabetes. 2010 Dec;59(12):2991-3. doi: 10.2337/db10-1149. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 21115781 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fawell SE, Lees JA, White R, Parker MG: Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell 1990;60:953–962 - PubMed
-
- Hayashi S, McMahon AP: Efficient recombination in diverse tissues by a tamoxifen-inducible form of Cre: a tool for temporally regulated gene activation/inactivation in the mouse. Dev Biol 2002;244:305–318 - PubMed
-
- Gannon M, Gamer LW, Wright CV: Regulatory regions driving developmental and tissue-specific expression of the essential pancreatic gene pdx1. Dev Biol 2001;238:185–201 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK057768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK074966/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071052/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD36720/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD036720/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK074966/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK20595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK66636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DK066636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069603/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK071052/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068764/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK066636/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK073716/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK072473/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057768/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK69603/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK071052/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK063363/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK065131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK072473/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK089572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK63363/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX000666/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- DK59637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK07563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK084236/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073716/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK065131/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

