Solid-state NMR and SAXS studies provide a structural basis for the activation of alphaB-crystallin oligomers
- PMID: 20802487
- PMCID: PMC2957905
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1891
Solid-state NMR and SAXS studies provide a structural basis for the activation of alphaB-crystallin oligomers
Abstract
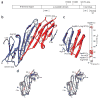
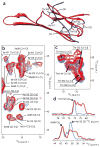
The small heat shock protein alphaB-crystallin (alphaB) contributes to cellular protection against stress. For decades, high-resolution structural studies on oligomeric alphaB have been confounded by its polydisperse nature. Here, we present a structural basis of oligomer assembly and activation of the chaperone using solid-state NMR and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). The basic building block is a curved dimer, with an angle of approximately 121 degrees between the planes of the beta-sandwich formed by alpha-crystallin domains. The highly conserved IXI motif covers a substrate binding site at pH 7.5. We observe a pH-dependent modulation of the interaction of the IXI motif with beta4 and beta8, consistent with a pH-dependent regulation of the chaperone function. N-terminal region residues Ser59-Trp60-Phe61 are involved in intermolecular interaction with beta3. Intermolecular restraints from NMR and volumetric restraints from SAXS were combined to calculate a model of a 24-subunit alphaB oligomer with tetrahedral symmetry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


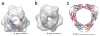
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

