Intrinsic biophysical diversity decorrelates neuronal firing while increasing information content
- PMID: 20802489
- PMCID: PMC2975253
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2630
Intrinsic biophysical diversity decorrelates neuronal firing while increasing information content
Abstract
Although examples of variation and diversity exist throughout the nervous system, their importance remains a source of debate. Even neurons of the same molecular type have notable intrinsic differences. Largely unknown, however, is the degree to which these differences impair or assist neural coding. We examined the outputs from a single type of neuron, the mitral cells of the mouse olfactory bulb, to identical stimuli and found that each cell's spiking response was dictated by its unique biophysical fingerprint. Using this intrinsic heterogeneity, diverse populations were able to code for twofold more information than their homogeneous counterparts. In addition, biophysical variability alone reduced pair-wise output spike correlations to low levels. Our results indicate that intrinsic neuronal diversity is important for neural coding and is not simply the result of biological imprecision.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that they have no competing interests.
Figures
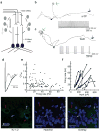
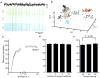
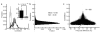
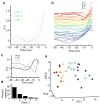


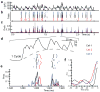
Comment in
-
It takes all kinds to make a brain.Nat Neurosci. 2010 Oct;13(10):1158-60. doi: 10.1038/nn1010-1158. Nat Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20877278 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ramon YC. Structure and connections of neurons. Bull Los Angel Neuro Soc. 1952;17:5–46. - PubMed
-
- Marder E, Goaillard JM. Variability, compensation and homeostasis in neuron and network function. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:563–574. - PubMed
-
- Gupta A, Wang Y, Markram H. Organizing principles for a diversity of GABAergic interneurons and synapses in the neocortex. Science. 2000;287:273–278. - PubMed
-
- Mainen ZF, Sejnowski TJ. Influence of dendritic structure on firing pattern in model neocortical neurons. Nature. 1996;382:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Schaefer AT, Larkum ME, Sakmann B, Roth A. Coincidence detection in pyramidal neurons is tuned by their dendritic branching pattern. J Neurophysiol. 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

